MSSQL INDEX Scan Principles and Methods
Today, I’m going to explain how to scan tables and indexes when executing a query.
Types of Index Scans
- Table full scan.
- Index full scan.
- Index unique scan.
- Index range scan.
- Index loose scan.
- Index merge scan.
INDEX scan features and description.
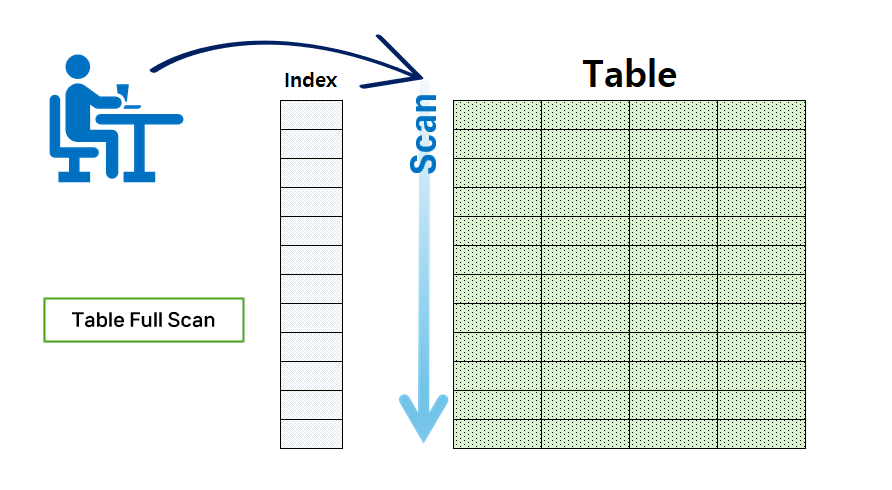
Table full scan
- This is a method that scans the data from beginning to end by going straight to the table data, regardless of whether there is an index.
- This occurs when there is no index on the table or there is no WHERE condition.
- This causes performance degradation when there is a large amount of data in the table.
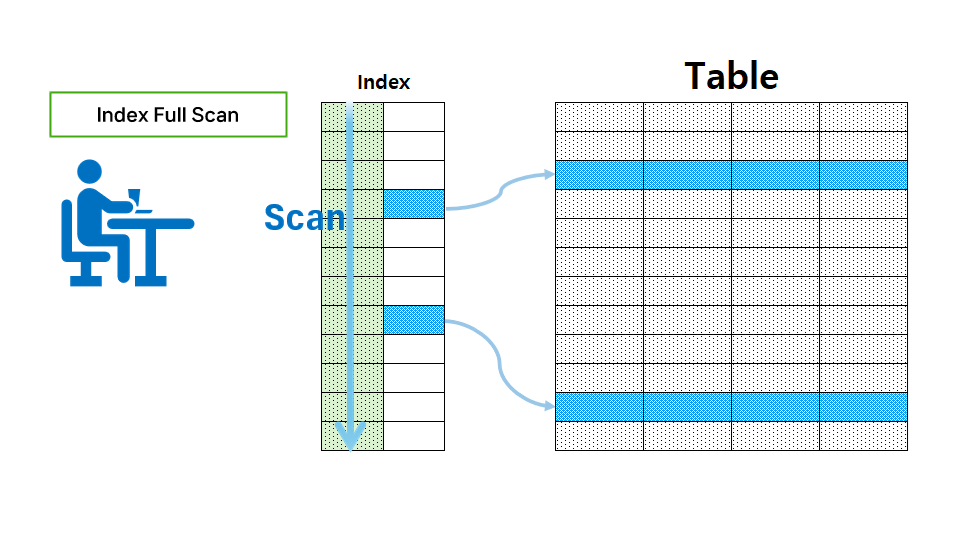
Index full scan
- A scan method that searches the index from beginning to end.
- Used when one or more index columns are used in the WHERE clause or when all columns used in SQL exist in one index.
- Used as a second option when there is no optimal index for data retrieval.
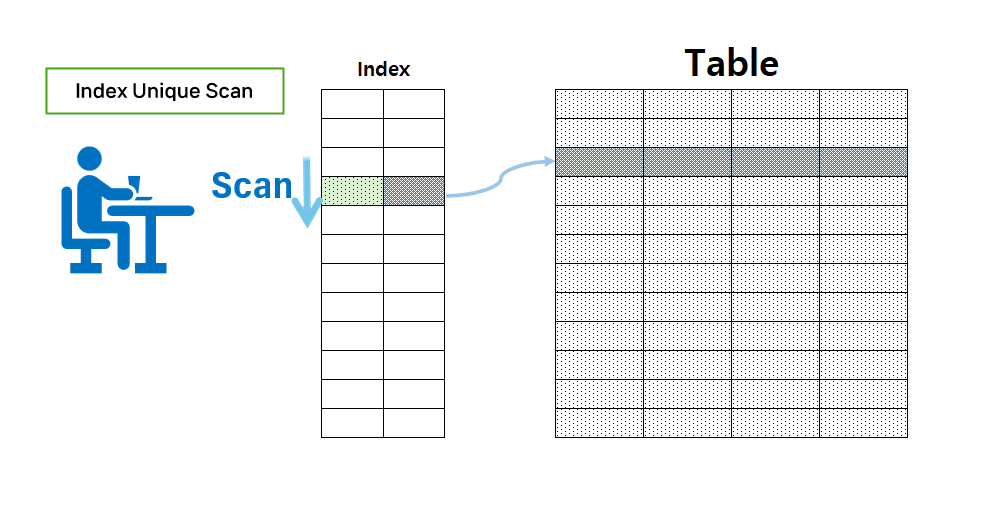
Index Unique Scan
- Possible when creating a Primark Key or when a Unique Index exists.
- Index Unique Scan can return data the fastest when searching using an index.
- The condition clause must have a condition for the key, and if there is a join clause, the condition must be entered in the column corresponding to the key.
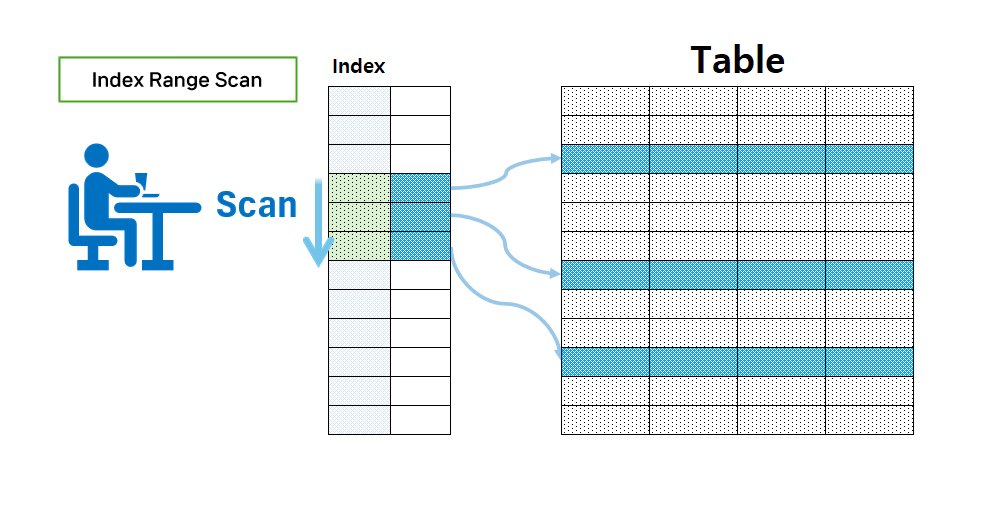
Index Range Scan
- This is a method of performing a range search on a column where an index is created.
- Most cases using comparison operators are usually processed in this way.
- For example, it is applied when there are <, <=, >, >=, between, like in the conditional clause.
- In order to increase the speed of Index Range Scan, it is important to reduce the range of the index scan by how much it can be reduced.
- In other words, the speed is key to how much the number of accesses can be reduced.
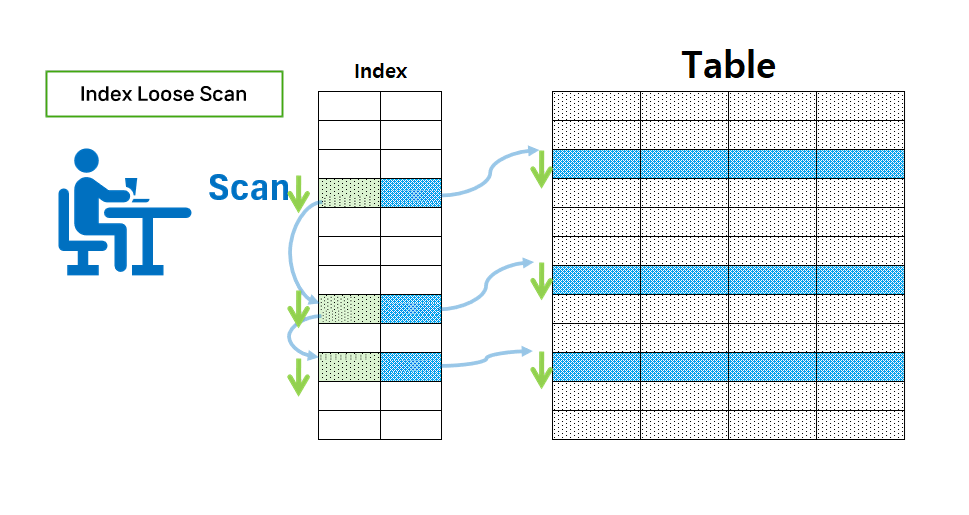
Index loose scan
- A method of scanning only the necessary parts of the index
- Scans only the necessary data based on the WHERE clause, and ignores the index keys of unnecessary data.
- And when the GROUP BY function, MAX(), MIN() function, etc. are used, the index loose scan operates.
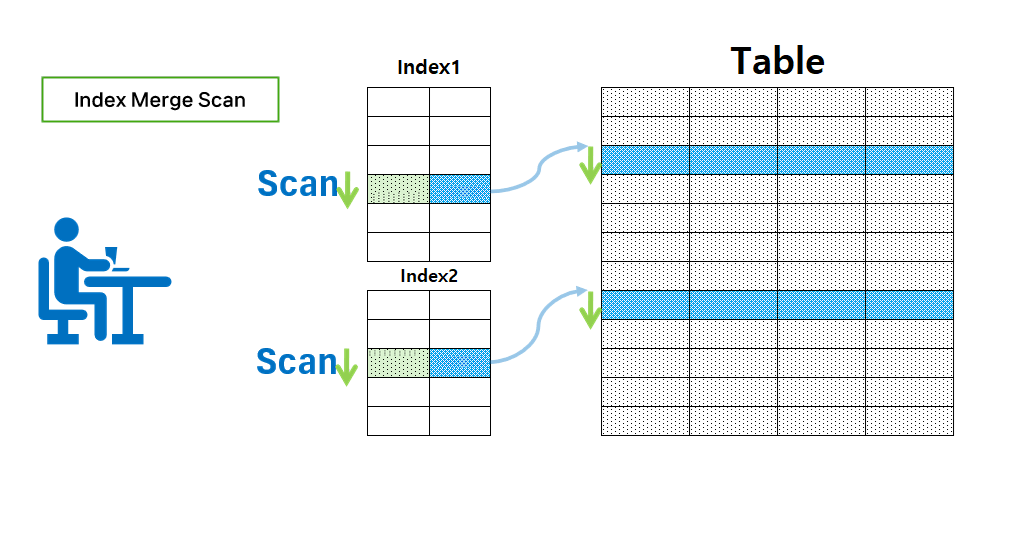
Index Merge Scan
- This is applied when using the ‘OR’ condition by integrating and scanning the indexes created within the table.
- This is the cause of performance degradation because each index is processed separately.
SELECT aurum_id, aurum_age
FROM dbo.aurum_indexScan
WHERE aurum_id = '1000' or aurum_age >= 10
;
Leave a comment