MSSQL Index Description and Index Types
Let’s explain the indexes that are frequently used to improve database performance and learn about the types of INDEX supported by SQL SERVER.
What is an INDEX?
- An index is a unique value that data has, and it means an index and list.
- An index displays attributes such as a unique key value, data name, data size, and the recording location when recording data.
- An index stores a key in a separate space and quickly returns the requested data when searching.
- INDEX is one of the important technologies used to increase the speed when searching data in a database.
- The difference between Clustered Index and Non-Clustered Index can be easily understood by looking at the picture below.
Types of Indexes.
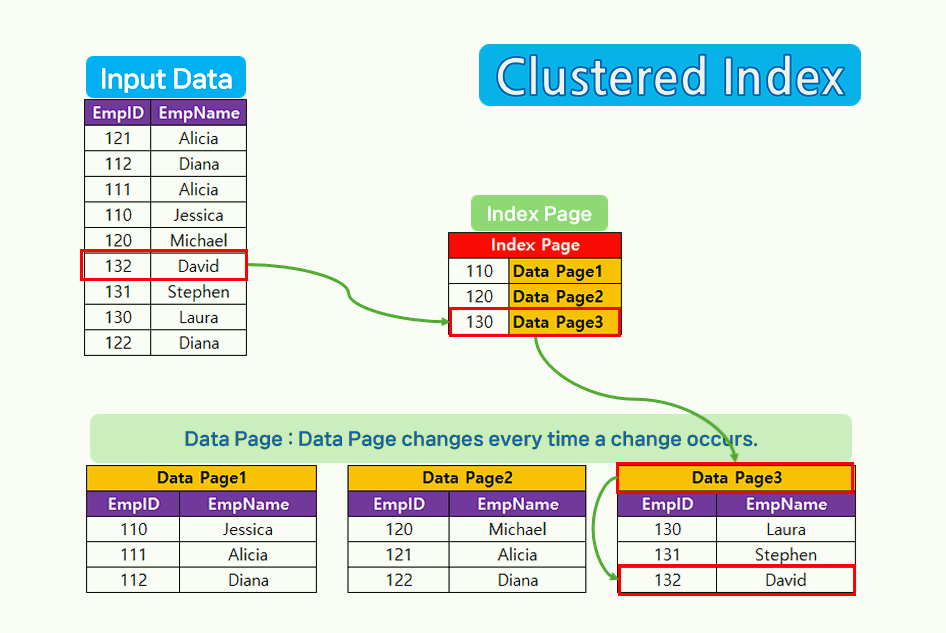
Clustered Index Features.
- Clustered Index is often explained using a book as an analogy. If you know which page it is, you can go straight to that page.
- Clustered Index sorts and stores data rows of a table or view based on the key value.
- Clustered Index can only create one Clustered Index per table.
- When a Clustered Index is created, the data rows of the table are physically rearranged based on the index key.
- When creating a Clustered Index, it is suitable for large tables that do not frequently have updates.
Clustered Index illustration.
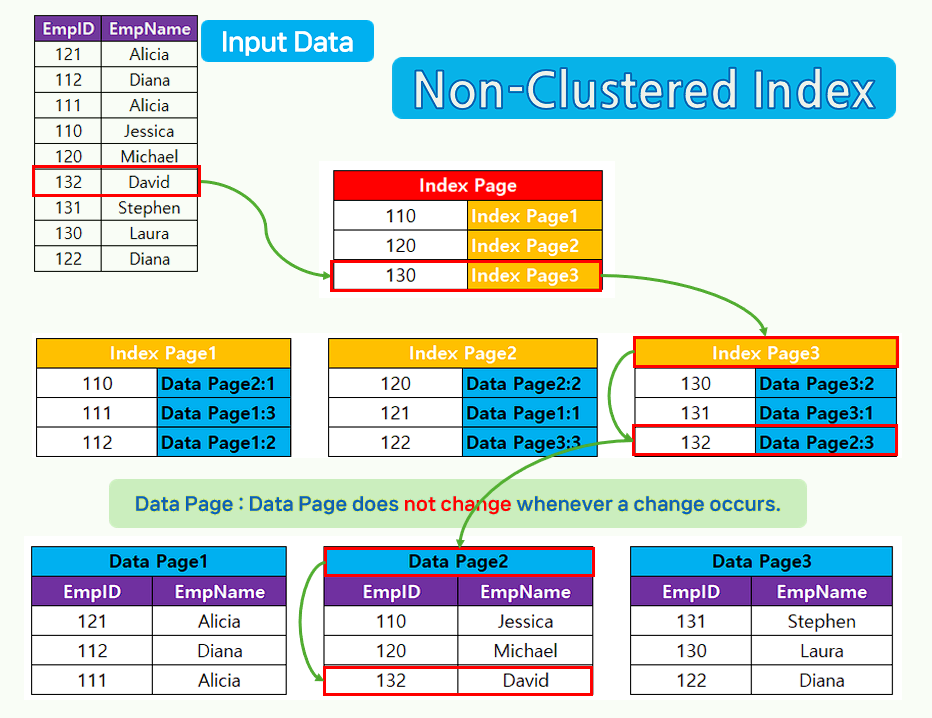
Non-Clustered Index Features.
- Non-Clustered Index does not sort data according to the physical order stored in the table.
- In other words, the data pages are not sorted in order.
- Non-Clustered Index leaves the data in the table as is and creates an index that sorts the specified columns. It does not touch the data pages.
- Non-Clustered Index is slow in search speed, but data input, modification, and deletion are fast.
- Clustered Index can exist only once in a table, but multiple Non-Clustered Indexes can be created.
Explanation of Non-Clustered Index with a picture.
Leave a comment