Difference between MSSQL stored procedures and user-defined functions
Let’s learn about the differences between user-defined functions and stored procedures, which play an important role in database programming.
What are procedures and user-defined functions?
- Procedures and user-defined functions are very helpful in keeping repetitive codes concise.
- Using procedures and user-defined functions is good for increasing the reusability of code.
- You can also use conditional statements (IF, CASE) and looping statements (WHILE).
- The difference between procedures and user-defined functions is that they can return values.
Difference between stored procedures and user-defined functions.
Stored procedures.
- Stored procedures are mainly used to manipulate and process data within a database.
- For example, tasks such as inserting, modifying, and deleting data can be performed using procedures.
- When performance improvement is required, procedures can help improve query execution speed.
- Procedures are used to manage transactions. Multiple queries can be combined into one transaction to ensure atomicity.
- Parameters used in procedures can be either input or output.
User-defined functions.
- Functions are used to perform specific calculations or transform values. - Functions must use a return clause.
- Parameters used in functions can be input.
- Procedures cannot be called within user-defined functions.
- User-defined functions can be used in SELECT, WHERE, HAVING clauses, etc.
- User-defined functions cannot use non-deterministic functions.
- For example, using try-catch, newid(), delete, update, print, etc. will cause an error.
- Function calls can degrade query performance.
How to execute stored procedures vs. user-defined functions.
Description of stored procedure vs. user-defined function source.
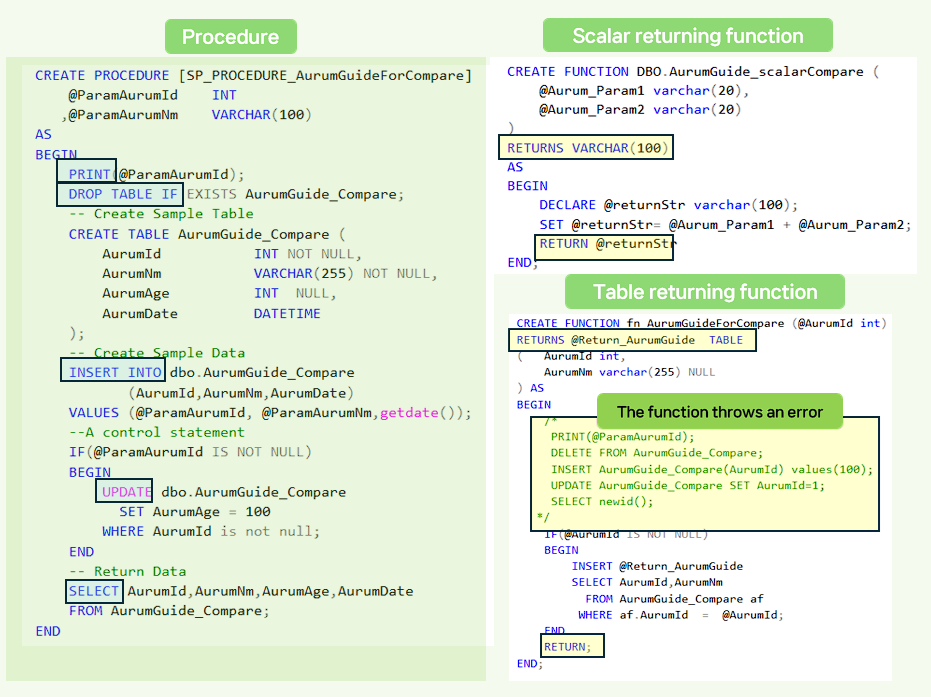
Stored procedure source and execution method.
-- DROP PROCEDURE [SP_PROCEDURE_AurumGuideForCompare]
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [SP_PROCEDURE_AurumGuideForCompare]
@ParamAurumId INT
,@ParamAurumNm VARCHAR(100)
AS
BEGIN
PRINT(@ParamAurumId);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS AurumGuide_Compare;
-- Create Sample Table
CREATE TABLE AurumGuide_Compare (
AurumId INT NOT NULL,
AurumNm VARCHAR(255) NULL,
AurumAge INT NULL,
AurumDate DATETIME
);
-- Create Sample Data
INSERT INTO dbo.AurumGuide_Compare
(AurumId,AurumNm,AurumDate)
VALUES (@ParamAurumId, @ParamAurumNm,getdate());
--A control statement
IF(@ParamAurumId IS NOT NULL)
BEGIN
UPDATE dbo.AurumGuide_Compare
SET AurumAge = 100
WHERE AurumId is not null;
END
-- Return Data
SELECT AurumId,AurumNm,AurumAge,AurumDate
FROM AurumGuide_Compare;
END
-- excute PROCEDURE
EXECUTE [dbo].[SP_PROCEDURE_AurumGuideForCompare] '198','function_compare';
User-defined function source and how to run it.
-- DROP FUNCTION fn_AurumGuideForCompare;
GO
CREATE FUNCTION fn_AurumGuideForCompare (@AurumId int)
RETURNS @Return_AurumGuide TABLE
(
AurumId int,
AurumNm varchar(255) NULL
) AS
BEGIN
/*
PRINT(@ParamAurumId);
DELETE FROM AurumGuide_Compare;
INSERT AurumGuide_Compare(AurumId) values(100);
UPDATE AurumGuide_Compare SET AurumId=1;
SELECT newid();
*/
IF(@AurumId IS NOT NULL)
BEGIN
INSERT @Return_AurumGuide
SELECT AurumId,AurumNm
FROM AurumGuide_Compare af
WHERE af.AurumId = @AurumId;
END
RETURN;
END;
GO
-- FUNCTION EXE
SELECT *
FROM DBO.fn_AurumGuideForCompare('10');
-----------------------------------------------
GO
--DROP FUNCTION DBO.AurumGuide_scalarCompare;
GO
CREATE FUNCTION DBO.AurumGuide_scalarCompare (
@Aurum_Param1 varchar(20),
@Aurum_Param2 varchar(20)
)
RETURNS VARCHAR(100)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @returnStr varchar(100);
SET @returnStr= @Aurum_Param1 + @Aurum_Param2;
RETURN @returnStr
END;
GO
-- FUNCTION EXE
SELECT DBO.AurumGuide_scalarCompare('Aurum','Guide');
Leave a comment