How to use MSSQL table-valued functions and scalar-valued functions
MSSQL functions can be largely divided into scalar return functions, inline table return functions, and multi-statement table return functions to return data.
Scalar, table-valued function features
Scalar return function features
- Rerun a single scalar value in a scalar function.
- A function that returns a single scalar value is usually called a scalar return function.
- It is easy to understand if you think of a scalar value as returning a single value.
- For example, the number 100, San Diego as a character, and similar to the OUT variable in a PROCEDURE.
Table-valued function features
- Inline table-valued function.
- You can determine the returned column in the select clause and return it.
- Since you have to write one QUERY statement, it cannot be used when it is multi-statement.
- Control statements cannot be used.
- In English, it is called inline table-valued function.
Multi-statement table-valued function.
- You can use multiple statements to specify the return value.
- You must write a QUERY statement within the begin, end delimiters.
- You can use most control statements, not just IF statements, so branching is possible.
- You must define the table to be returned.
- You must end with a return statement at the end.
- For example, if you declare 5 columns in a table, you can only return data for 5 columns.
- In English, it is called Multi-statement table-valued function(MSTVFs).
How to use scalar and table-valued functions
Explanation of the difference between scalar and table-valued functions.
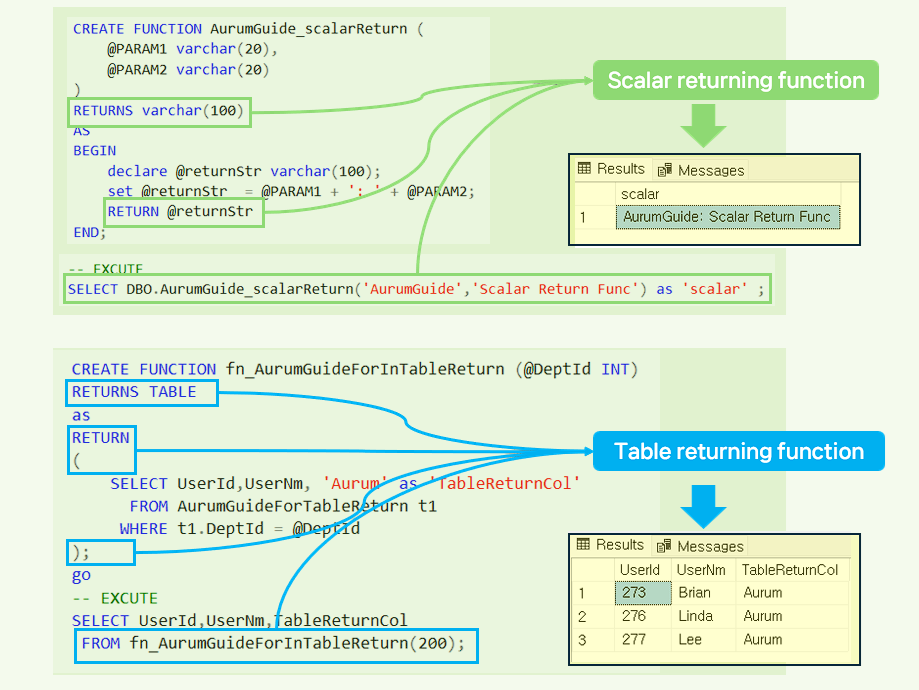
- How to use scalar function.
-- DROP FUNCTION AurumGuide_scalarReturn;
CREATE FUNCTION AurumGuide_scalarReturn (
@PARAM1 varchar(20),
@PARAM2 varchar(20)
)
RETURNS varchar(100)
AS
BEGIN
declare @returnStr varchar(100);
set @returnStr = @PARAM1 + ': ' + @PARAM2;
RETURN @returnStr
END;
-- EXCUTE
SELECT DBO.AurumGuide_scalarReturn('AurumGuide','Scalar Return Func') as 'scalar' ;
- How to use inline table-valued functions.
-- 1. CREATE TABLE
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS AurumGuideForTableReturn;
CREATE TABLE AurumGuideForTableReturn (
UserId INT,
UserNm VARCHAR(255) NULL,
DeptId INT
);
INSERT INTO dbo.AurumGuideForTableReturn(UserId,UserNm,DeptId)
VALUES (272, N'Ken',100)
,(273, N'Brian',200)
,(276, N'Linda',200)
,(277, N'Lee',200);
--drop FUNCTION fn_AurumGuideForInTableReturn;
go
--Example of an inline table-valued function.
CREATE FUNCTION fn_AurumGuideForInTableReturn (@DeptId INT)
RETURNS TABLE
as
RETURN
(
SELECT UserId,UserNm, 'Aurum' as 'TableReturnCol'
FROM AurumGuideForTableReturn t1
WHERE t1.DeptId = @DeptId
);
go
-- EXCUTE
SELECT UserId,UserNm,TableReturnCol
FROM fn_AurumGuideForInTableReturn(200);
- How to use a multi-sentence table-returning function.
--Example of a multi-sentence table-returning function.
--DROP FUNCTION fn_AurumGuideForMulTableReturn;
CREATE FUNCTION fn_AurumGuideForMulTableReturn (@UserId int)
RETURNS @Return_AurumGuide TABLE
(
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255) NULL
) AS
BEGIN
IF(@UserId = '')
BEGIN
INSERT @Return_AurumGuide
SELECT UserId,UserNm
FROM AurumGuideForTableReturn af;
END
ELSE
BEGIN
INSERT @Return_AurumGuide
SELECT UserId,UserNm
FROM AurumGuideForTableReturn af
WHERE af.UserId = @UserId ;
END
RETURN;
END;
-- EXCUTE
SELECT *
FROM fn_AurumGuideForMulTableReturn('');
-- EXCUTE
SELECT *
FROM fn_AurumGuideForMulTableReturn('273');
Leave a comment