mssql function features and description
MSSQL functions are used when receiving parameters, performing data retrieval, modification, deletion, and operation processes within the function, and then returning the results.
Description of MSSQL function types
System function types and descriptions.
- Functions supported by SQL Server are called system-defined functions.
- String functions change string type data, such as CHARINDEX(), REPLACE(), LTRIM(), RTRIM(), LEN(), LEFT(), RIGHT(), LOWER(), etc.
- Aggregate functions mainly perform data operations, such as COUNT(), MAX(), MIN(), SUM(), etc.
- Date functions and time functions are used when changing date and time data.
- For detailed information on functions, refer to the MSSQL Date Function, Time Function Usage Summary and Description.
- How to use and explain MSSQL date and time functions
- In addition, SQL Server supports cursor functions, graph functions, JSON functions, and mathematical functions.
User-defined functions.
- User-defined functions are classified into scalar functions and table-valued functions depending on the form in which they return data.
- Scalar functions are functions that return a single scalar value.
- For example, the LEN() function, which returns the length of a string column, and the REPLACE() function, which can change a string, are representative examples.
- Table-valued functions return data types and are classified into inline table-valued functions and multi-statement table-valued functions.
- They are used when returning data in table form. If you refer to the example below, you can understand them more easily.
MSSQL function usage and examples
System function usage.
- System function usage examples.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS AurumGuideForFunction;
CREATE TABLE AurumGuideForFunction (
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255) NOT NULL,
UserAge int NULL,
DeptId varchar(500) NULL
);
INSERT INTO dbo.AurumGuideForFunction(UserId,UserNm,UserAge,DeptId)
VALUES (272, N'Ken',10,100)
,(274, N'Stephen',20,100)
,(275, N'Michael',30,200)
,(276, N'Linda',40,200)
,(277, N'Lee',40,100);
-- How to use system functions.
--String functions
SELECT LEN('AurumGuide') as lenFunc
,LOWER('AurumGuide') as lowerFunc
;
-- Aggregate function
SELECT SUM(UserAge) as sumFunc
,MIN(UserAge) as minFunc
,MAX(UserAge) as maxFunc
FROM dbo.AurumGuideForFunction
;
-- Login function (the time the user last changed his password)
SELECT LOGINPROPERTY('sa', 'PasswordLastSetTime');
-- System table return function (authorization check)
SELECT *
FROM sys.fn_my_permissions(NULL, 'DATABASE');
User-defined scalar functions.
- Example of using scalar functions.
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.AurumGuide_scalarFunction (@PARAM1 INT, @PARAM2 INT)
RETURNS INT
AS
BEGIN
RETURN @PARAM1 + @PARAM2
END;
go
-- EXCUTE
select dbo.AurumGuide_scalarFunction(10,20);
Inline table return function.
- Example of using inline table return.
-- Inline table return
CREATE FUNCTION fn_AurumGuide_InlineTableFunction (@DeptId INT)
RETURNS TABLE
as
RETURN
(
SELECT UserId,UserNm,UserAge,DeptId
FROM AurumGuideForFunction t1
WHERE t1.DeptId = @DeptId
)
;
go
-- EXCUTE
select *
from fn_AurumGuide_InlineTableFunction(100);
Multiple sentence table return function.
- Detailed explanation of the source code for returning multiple sentence tables.
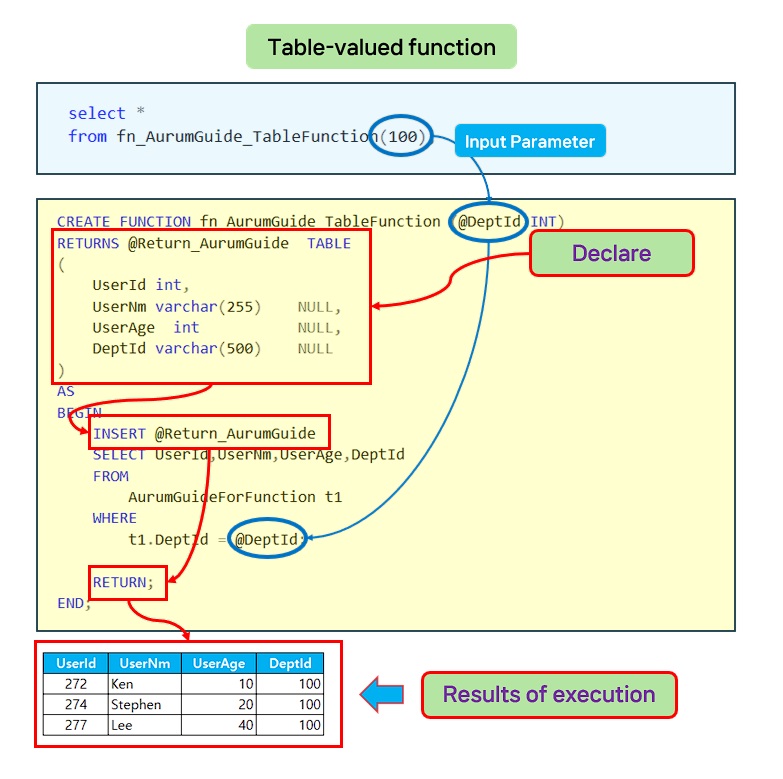
- Example of using a multi-sentence table return.
-- Multi-sentence table return function
CREATE FUNCTION fn_AurumGuide_TableFunction (@DeptId INT)
RETURNS @Return_AurumGuide TABLE
(
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255) NULL,
UserAge int NULL,
DeptId varchar(500) NULL
)
AS
BEGIN
INSERT @Return_AurumGuide
SELECT UserId,UserNm,UserAge,DeptId
FROM AurumGuideForFunction t1
WHERE t1.DeptId = @DeptId;
RETURN;
END;
go
-- EXCUTE
select *
from fn_AurumGuide_TableFunction(100);
MSSQL Function Notes
- User-defined functions have the advantage of being able to use the source code concisely.
- However, if they are used inappropriately, they can cause performance problems.
- When using a table return function, we recommend checking the returned DATA and using it.
- Repeatedly returning a lot of data can cause system failure.
Leave a comment