How to use procedure parameters
MSSQL stored procedures can receive parameters and return values through OUTPUT parameters.
Features of stored procedure parameters.
Input parameter features.
- This is a parameter that allows the values entered during execution to be used within the stored procedure.
- You can also set a default value for the parameter when declaring it.
- If IN or OUT is omitted, it is recognized as an input parameter.
- You must declare a type after the parameter name.
Output parameter features.
- Output parameters are used to output the return value executed within the stored procedure.
- You must specify it with the OUTPUT keyword when declaring stored procedure parameters. The default value is input.
How to use stored procedure parameters.
Input parameter example.
- Declare the parameters of the stored procedure and execute the procedure.
--Here is an example of input parameters.
-- DROP PROCEDURE [STORE_PROCEDURE_IN_PARAMETER];
CREATE PROCEDURE [DBO].[STORE_PROCEDURE_IN_PARAMETER]
@UserAge INT ,
@UserName VARCHAR(100) = 'Lee'
AS
BEGIN
-- Parameter print.
SELECT @UserAge, @UserName;
END;
-- EXCUTE EX1
EXEC STORE_PROCEDURE_IN_PARAMETER @UserAge = 2;
-- EXCUTE EX2
EXEC STORE_PROCEDURE_IN_PARAMETER @UserAge = 2, @UserName= 'john';
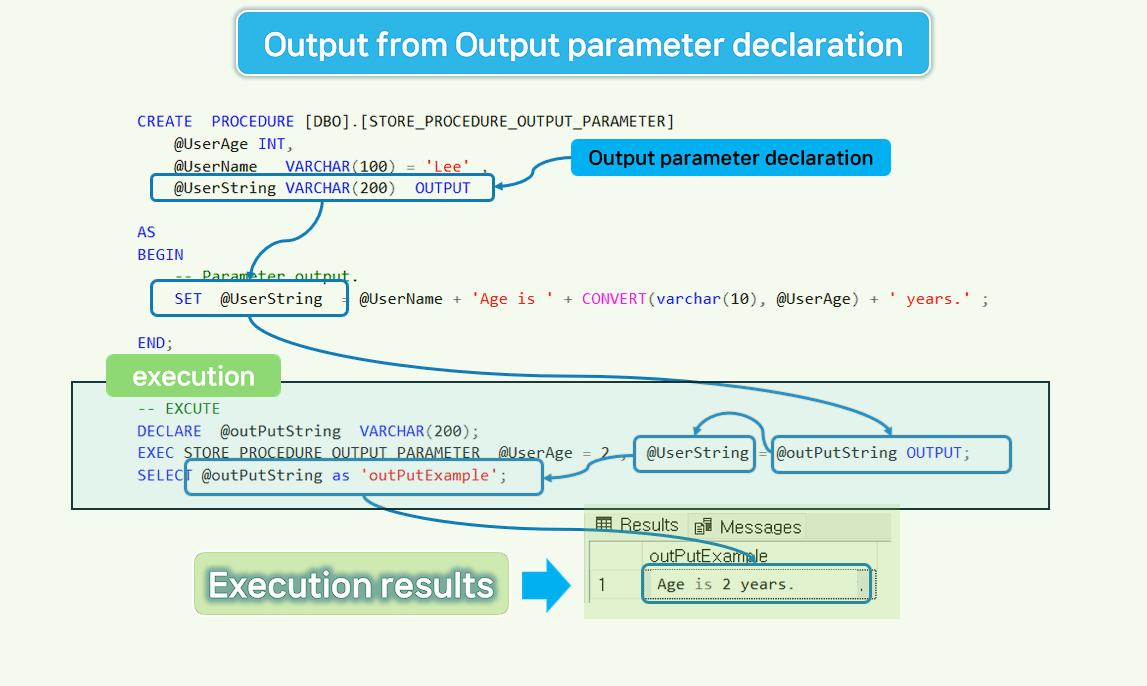
Here is an example of an output parameter.
- Declare output parameters of stored procedures and return values.
-- Example of output parameters.
-- DROP PROCEDURE DBO.STORE_PROCEDURE_OUTPUT_PARAMETER;
CREATE PROCEDURE [DBO].[STORE_PROCEDURE_OUTPUT_PARAMETER]
@UserAge INT,
@UserName VARCHAR(100) = 'Lee' ,
@UserString VARCHAR(200) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
-- Parameter output.
SET @UserString = @UserName + ''s age is ' + CONVERT(varchar(10), @UserAge) + ' years.' ;
END;
-- EXCUTE
DECLARE @outPutString VARCHAR(200);
EXEC STORE_PROCEDURE_OUTPUT_PARAMETER @UserAge = 2 , @UserString = @outPutString OUTPUT;
SELECT @outPutString as 'outPutExample';
Finishing the stored procedure parameters.
Executing when there are no stored procedure parameters.
- Stored procedures can be used even without parameters.
- For example, suppose that the operations of table A and table B are inserted into table C,
- There is no need to input parameters for work purposes, and only the stored procedure can be executed.
Leave a comment