How to debug stored procedures
I think MSSQL is too hard to debug stored procedures, so I’m going to explain how to debug stored procedures simply.
Stored procedure debugging types
- The procedure debugging method using the PRINT statement is the most commonly used method to check values, and it uses the print statement at the necessary points to check values.
- The procedure debugging method using the SELECT statement is usually used when using dynamic queries, and is used when printing the executed statement and parameters.
- RAISERROR can check values while showing error messages at specific points.
- DEBUG FLAG is a method of debugging by adding it when declaring parameters in the procedure and then changing the DEBUG FLAG when executing.
How to debug stored procedures and examples
How to debug procedures using the PRINT statement.
- You can check the contents printed by PRINT in Messages.
- This is an example of the PRINT statement source.
CREATE TABLE UserInfoForDebugging (
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255) NOT NULL,
UserAge int
);
GO
INSERT INTO dbo.UserInfoForDebugging(UserId,UserNm,UserAge)
VALUES (272, N'Ken',10)
,(273, N'Brian',34)
,(274, N'Debugging',45)
,(275, N'Michael',65)
,(276, N'Linda',12);
GO
-- How to debug a procedure using the PRINT statement.
-- DROP PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_PRINT]
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_PRINT]
@UserNm NVARCHAR(10)
AS
BEGIN
PRINT('userNmValue:' + @UserNm);
SELECT *
FROM UserInfoForDebugging
WHERE UserNm = @UserNm;
END;
GO
-- Run the source
EXECUTE DBO.[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_PRINT] 'Debugging';
How to debug a procedure using the SELECT statement.
- The SELECT statement checks the query that is executed when using dynamic query.
- If the stored procedure source is an Insert statement, you can comment out the execution statement and check it by inserting only the SELECT clause.
- This is an example of the SELECT statement source.
-- How to debug a procedure using the SELECT statement.
-- DROP PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_SELECT];
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_SELECT]
@ParamUserId INT
,@ParamUserNm VARCHAR(100)
,@ParamUserAge INT
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @InsertString NVARCHAR(500);
DECLARE @ParmDefinition NVARCHAR(500);
SET @InsertString = ' INSERT INTO dbo.UserInfoForDebugging '
+ ' ( UserId,UserNm,UserAge ) ';
IF(@ParamUserAge > 20 )
BEGIN
SET @InsertString += ' VALUES ( @StmtParamUserId, @StmtParamUserNm, 30 );'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @InsertString += ' VALUES ( @StmtParamUserId, @StmtParamUserNm, 15 );'
END
SET @ParmDefinition = N'@StmtParamUserId INT,
@StmtParamUserNm VARCHAR(100)
';
-- This is for debugging procedures using SELECT statements.
SELECT 'InsertString : ' + @InsertString;
EXEC sp_executesql @InsertString,
@ParmDefinition,
@ParamUserId,
@ParamUserNm
END
-- Run the source
EXECUTE DBO.STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_SELECT 10, 'DEBUGGING_SELECT',24
RAISERROR debugging example.
- RAISERROR is used with TRY CATCH statement.
- RAISERROR source example.
-- RAISERROR debugging example.
-- DROP PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_RAISERROR]
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_RAISERROR]
@UserAge NVARCHAR(10)
AS
BEGIN
BEGIN TRY
SELECT UserAge / @UserAge AS ' ERROR '
FROM UserInfoForDebugging;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
RAISERROR('Error occurred', 10, 1);
END CATCH
END;
GO
-- RAISERROR ERROR
EXECUTE DBO.[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_RAISERROR] @UserAge = 0;
GO
-- NO ERROR --> OK
EXECUTE DBO.[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_RAISERROR] @UserAge = 1;
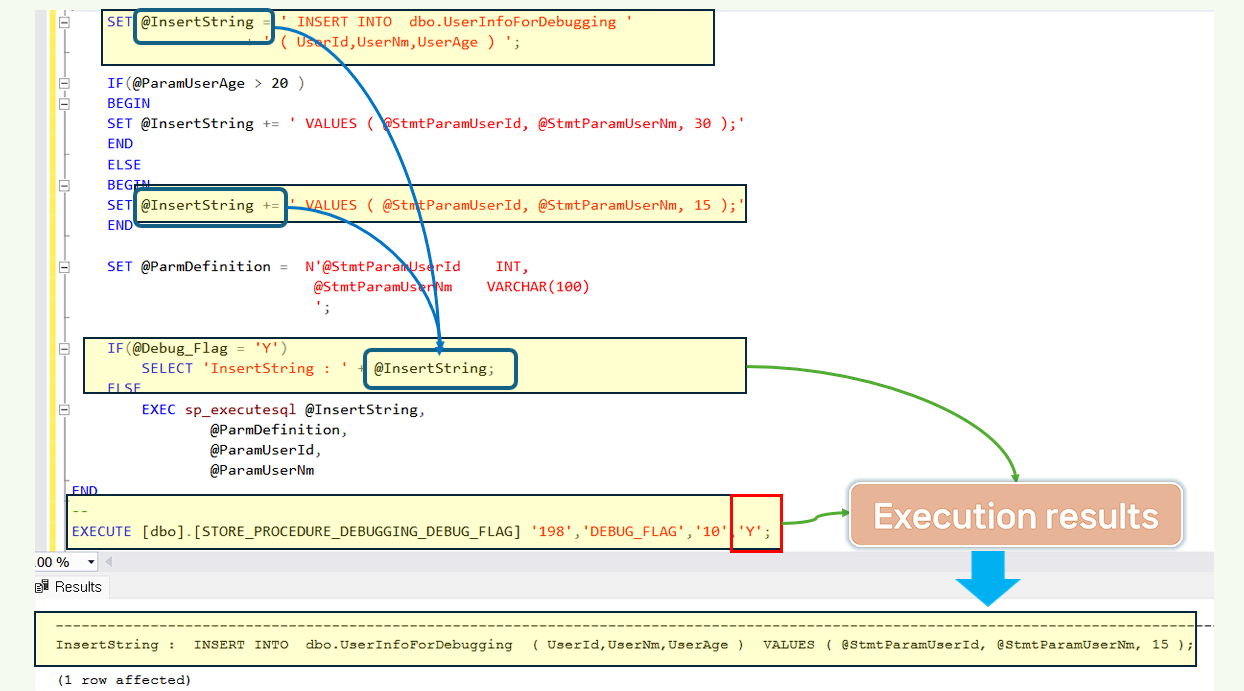
Debugging example using DEBUG FLAG.
- Debugging using DEBUG FLAG requires parameters for debugging when creating a stored procedure.
- Debugging using DEBUG FLAG allows you to debug by changing parameter values without modifying the original source.
- DEBUG FLAG source.
-- Debugging example using DEBUG FLAG.
-- DROP PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_DEBUG_FLAG];
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_DEBUG_FLAG]
@ParamUserId INT
,@ParamUserNm VARCHAR(100)
,@ParamUserAge INT
,@Debug_Flag VARCHAR(1)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @InsertString NVARCHAR(500);
DECLARE @ParmDefinition NVARCHAR(500);
SET @InsertString = ' INSERT INTO dbo.UserInfoForDebugging '
+ ' ( UserId,UserNm,UserAge ) ';
IF(@ParamUserAge > 20 )
BEGIN
SET @InsertString += ' VALUES ( @StmtParamUserId, @StmtParamUserNm, 30 );'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @InsertString += ' VALUES ( @StmtParamUserId, @StmtParamUserNm, 15 );'
END
SET @ParmDefinition = N'@StmtParamUserId INT,
@StmtParamUserNm VARCHAR(100)
';
IF(@Debug_Flag = 'Y')
SELECT 'InsertString : ' + @InsertString;
ELSE
EXEC sp_executesql @InsertString,
@ParmDefinition,
@ParamUserId,
@ParamUserNm
END
-- Run the source
EXECUTE [dbo].[STORE_PROCEDURE_DEBUGGING_DEBUG_FLAG] '198','DEBUG_FLAG','10','Y'
Finishing procedure debugging
Debugging using tools?
- Basically, SSMS, Visual Studio, etc. are supported, but they are not practical, so I do not recommend them.
- If you have a good tool, please recommend it in the reply.
Leave a comment