Stored Procedure Advantages and Disadvantages Explained
Stored Procedures are compiled in the database and stored on the database server, so they have advantages but disadvantages, so I will explain them.
Stored Procedure Advantages and Disadvantages
Stored Procedure Advantages.
- In terms of database performance, since Procedures are basically compiled upon first execution, performance is improved because the execution plan can be reused.
- Stored Procedures can execute multiple SQL statements with a single request, so they are convenient to use.
- Since SQL logic is managed centrally in the database, maintenance is easy.
- In terms of security, it is secure because it calls stored procedures instead of calling direct SQL statements.
Stored Procedure Disadvantages.
- Debugging when an error occurs is much more difficult than general SQL.
- Stored Procedures depend on the platform of each database company, so they must be developed according to the database that changes when another database system is changed.
- There are advantages to writing multiple SQLs at once, but the logic becomes complicated, making maintenance difficult.
- Stored Procedures depend on the database, so they are applied immediately, which can be dangerous.
- Maintenance becomes difficult when dynamic SQL is frequently used. - Stored Procedure If a lot of operation logic is included, CPU usage may increase, which may cause performance problems.
Stored Procedure Execution Process
Stored Procedure Execution Flowchart.
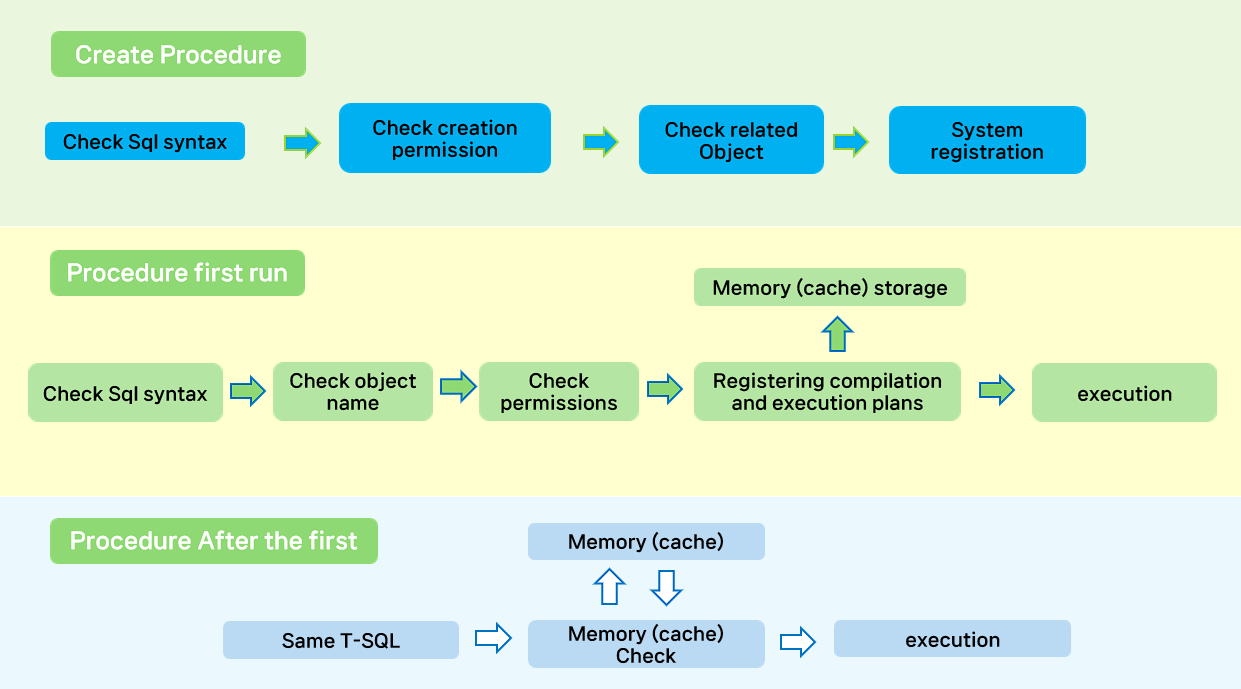
When creating a stored procedure.
- Check SQL syntax: Check the SQL written in the stored procedure.
- However, if it is inside a string in dynamic SQL, it cannot be checked.
- Check creation permission: Check if the database has permission to create a stored procedure.
- Check related objects: Check if there is a related table when it is static SQL.
- Register in the system: Register the procedure in the system table.
First execution of a stored procedure.
- Check SQL syntax: Check the execution SQL based on the SQL written in the stored procedure.
- Check object name: Check if the corresponding stored procedure exists in the system.
- Check permission: Check the execution permission of the stored procedure.
- Register compilation and execution plan: Compile T-SQL and create an execution plan.
- Save memory (cache): Save the execution plan.
- Execute: Execute the written T-SQL statement.
Stored Procedure Executed After First Time.
- Same T-SQL: If there is the same T-SQL.
- Check memory (cache): Check the memory if there is an execution plan registered in the first execution.
- Execute: Executes T-SQL statements.
Stored Procedure Pros and Cons Summary
- Stored procedures have many advantages when the business logic is simple, but they have many management problems when they become complex.
- However, there are times when they must be used due to the nature of the work, so we recommend using them as needed.
- When using parameters like Dynamic SQL, you should write them considering the order.
- When using IF statements, CASE statements, and While statements in Stored Procedures, you should write them considering maintenance or performance.
- When using Dynamic SQL, we recommend SP_executesql.
Leave a comment