sp_executesql usage and parameters
sp_executesql is a command that allows you to efficiently execute queries that include parameters and is mainly used in Transact-SQL statements or stored procedures.
Features of sp_executesql
- sp_executesql is very efficient when executing dynamic queries and can use parameters.
- The query statement that is executed is not precompiled until the sp_executesql statement is executed, and when called with sp_executesql, the query statement is compiled into a separate execution plan and executed.
- That is, when executing Transact-SQL statements multiple times, the execution plan can be precompiled and reused.
- Parameters include Unicode strings, so multilingual data can be processed.
- sp_executesql has improved EXECUTE, has stronger security, and has a lower compilation load, so sp_executesql is mainly recommended these days.
How to use sp_executesql
Executing a dynamically built string.
- This is the process of putting dynamic SQL in a variable and declaring parameters in sp_executesql to execute it.
- This is the sp_executesql execution flow chart.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS InfoForSp_executesql;
CREATE TABLE InfoForSp_executesql (
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255),
UserAge int ,
InOutType varchar(10)
);
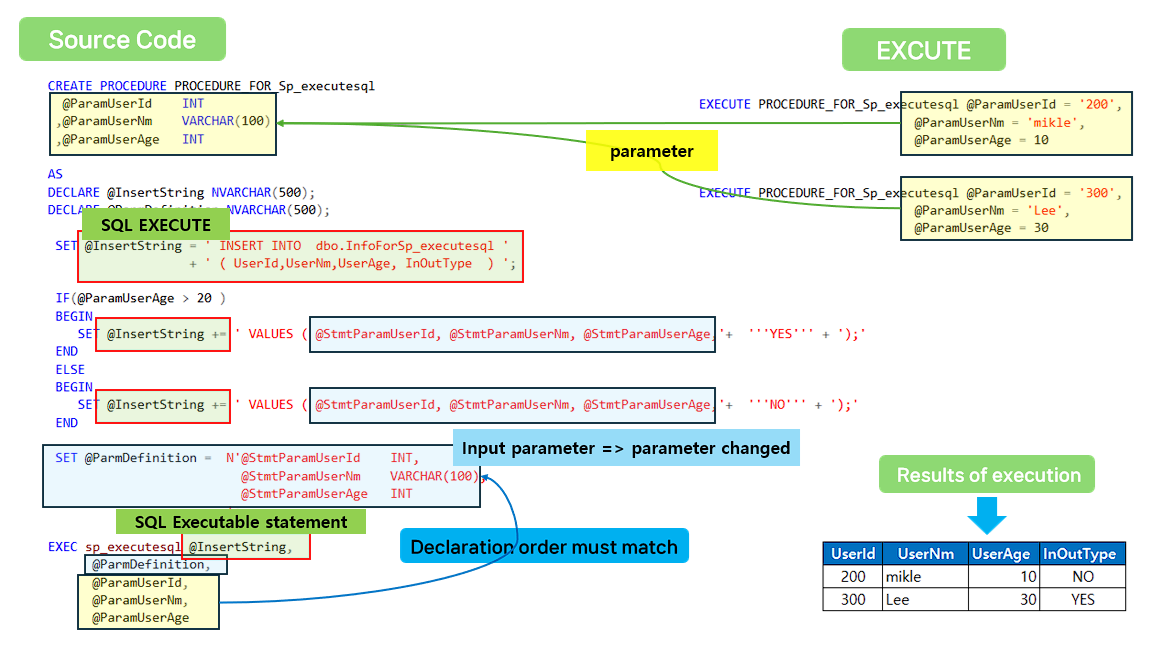
CREATE PROCEDURE PROCEDURE_FOR_Sp_executesql
@ParamUserId INT
,@ParamUserNm VARCHAR(100)
,@ParamUserAge INT
AS
DECLARE @InsertString NVARCHAR(500);
DECLARE @ParmDefinition NVARCHAR(500);
SET @InsertString = ' INSERT INTO dbo.InfoForSp_executesql '
+ ' ( UserId,UserNm,UserAge, InOutType ) ';
IF(@ParamUserAge > 20 )
BEGIN
SET @InsertString += ' VALUES ( @StmtParamUserId, @StmtParamUserNm, @StmtParamUserAge,'+ '''YES''' + ');'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @InsertString += ' VALUES ( @StmtParamUserId, @StmtParamUserNm, @StmtParamUserAge,'+ '''NO''' + ');'
END
SET @ParmDefinition = N'@StmtParamUserId INT,
@StmtParamUserNm VARCHAR(100),
@StmtParamUserAge INT
';
EXEC sp_executesql @InsertString,
@ParmDefinition,
@ParamUserId,
@ParamUserNm,
@ParamUserAge
-- EXECUTE
EXECUTE PROCEDURE_FOR_Sp_executesql @ParamUserId = '200',
@ParamUserNm = 'mikle',
@ParamUserAge = 10 ;
-- EXECUTE
EXECUTE PROCEDURE_FOR_Sp_executesql @ParamUserId = '300',
@ParamUserNm = 'Lee',
@ParamUserAge = 30 ;
SELECT *
FROM dbo.InfoForSp_executesql;
Setting parameter values separately from Transact-SQL strings.
- Example of using sp_executesql in Transact-SQL.
INSERT INTO dbo.InfoForSp_executesql(UserId,UserNm,UserAge,InOutType) VALUES
(272, N'Ken',35,'')
,(273, N'Brian',70,'')
,(274, N'Stephen',30,'')
,(275, N'Michael',53,'')
,(276, N'Linda',34,'');
-- Set parameter values separately from Transact-SQL strings.
DECLARE @IntVariable INT;
DECLARE @SQLString NVARCHAR(500);
DECLARE @ParmDefinition NVARCHAR(500);
SET @SQLString =
N' SELECT UserId,UserNm,UserAge
FROM InfoForSp_executesql
WHERE UserId = @UserId';
SET @ParmDefinition = N'@UserId INT';
SET @IntVariable = 272;
EXECUTE sp_executesql @SQLString, @ParmDefinition,
@UserId = @IntVariable;
Using the OUTPUT parameter.
- Parameters can be not only input, but can also output data as OUTPUT parameters.
-- Using the OUTPUT parameter.
DECLARE @SQLString NVARCHAR(500);
DECLARE @ParmDefinition NVARCHAR(500);
DECLARE @OutPutName NVARCHAR(25);
DECLARE @IntVariable INT;
SET @SQLString = N'SELECT @UserNmrOUT = MAX(UserNm)
FROM InfoForSp_executesql
WHERE UserId = @ParamUserId ';
SET @ParmDefinition = N'@ParamUserId INT,
@UserNmrOUT NVARCHAR(25) OUTPUT';
SET @IntVariable = 300;
EXECUTE sp_executesql
@SQLString
,@ParmDefinition
,@ParamUserId = @IntVariable
,@UserNmrOUT = @OutPutName OUTPUT;
-- This SELECT statement returns the value of the OUTPUT parameter.
SELECT @OutPutName;
Organizing the sp_executesql command
- Before sp_executesql came out, the EXECUTE statement often had security issues, but with MSSQL supporting sp_executesql, the supplementary issues have been eliminated.
- When using Dynamic SQL, sp_executesql is usually used.
Leave a comment