MSSQL OUTPUT clause usage and utilization
The MSSQL OUTPUT clause allows you to check query results in real time and use them for other tasks, maintaining data integrity and increasing the efficiency of database operations.
MSSQL OUTPUT clause utilization
Data audit function.
- You can save data changes to a table of your choice using the OUTPUT clause. In other words, it is very efficient in saving the history of data changes.
- The use of the OUTPUT clause increases the transparency of database operations and is utilized to track data changes in real time.
- You can also use the INTO keyword to store the returned data in another table.
- In INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements, you can compare the original data of the changed or deleted DATA with the new data.
Checking data during a transaction.
- You can use the OUTPUT clause in a transaction to retrieve intermediate data and write additional logic.
- In other words, it plays an important role in understanding the flow of data in a complex transaction structure.
Interaction with temporary tables.
- You can insert data into a temporary table using the OUTPUT clause and then use it for other queries.
Combination with the MERGE statement.
- When using the MERGE statement, you can use the OUTPUT clause to obtain information about each inserted, updated, or deleted row.
MSSQL OUTPUT Clause Example
Using the OUTPUT Clause with the DELETE Statement.
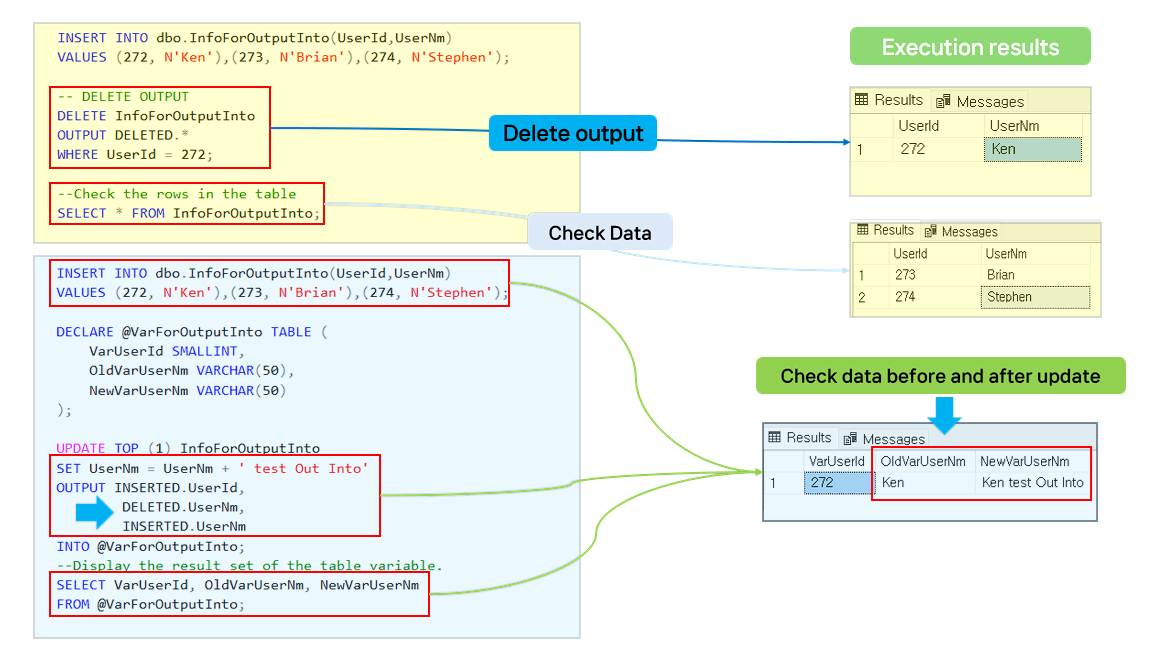
- OUTPUT DELETED.* can check the deleted data.
- OUTPUT DELETED source example.
--Use OUTPUT with a DELETE statement
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS InfoForOutputInto;
CREATE TABLE InfoForOutputInto (
UserId SMALLINT,
UserNm VARCHAR(50)
);
INSERT INTO dbo.InfoForOutputInto(UserId,UserNm)
VALUES (272, N'Ken'),(273, N'Brian'),(274, N'Stephen');
-- DELETE OUTPUT
DELETE InfoForOutputInto
OUTPUT DELETED.*
WHERE UserId = 272;
--Check the rows in the table
SELECT * FROM InfoForOutputInto;
Using OUTPUT INTO with UPDATE statement.
- Using OUTPUT clause, you can check the values that existed before applying UPDATE statement in DELETED column and updated values in INSERTED column in table variable.
- OUTPUT INTO UPDATE source example.
-- Use OUTPUT INTO with an UPDATE statement
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS InfoForOutputInto;
CREATE TABLE InfoForOutputInto (
UserId SMALLINT,
UserNm VARCHAR(50)
);
INSERT INTO dbo.InfoForOutputInto(UserId,UserNm)
VALUES (272, N'Ken'),(273, N'Brian'),(274, N'Stephen');
DECLARE @VarForOutputInto TABLE (
VarUserId SMALLINT,
OldVarUserNm VARCHAR(50),
NewVarUserNm VARCHAR(50)
);
UPDATE TOP (1) InfoForOutputInto
SET UserNm = UserNm + ' test Out Into'
OUTPUT INSERTED.UserId,
DELETED.UserNm,
INSERTED.UserNm
INTO @VarForOutputInto;
--Display the result set of the table variable.
SELECT VarUserId, OldVarUserNm, NewVarUserNm
FROM @VarForOutputInto;
Using OUTPUT INTO with INSERT statement.
- You can insert data into a specified table and use the OUTPUT clause to insert the result into a table variable, then check the entered data.
- This is an example of OUTPUT INTO INSERT source.
-- Use OUTPUT INTO with an INSERT statement
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS InfoForOutputInto;
CREATE TABLE InfoForOutputInto (
UserId SMALLINT,
UserNm VARCHAR(50),
ModiDate DATETIME
);
DECLARE @VarForOutputIntoInsert TABLE (
VarUserId SMALLINT,
VarUserNm VARCHAR(50),
VarModiDate DATETIME);
INSERT InfoForOutputInto
OUTPUT INSERTED.UserId, INSERTED.UserNm, INSERTED.ModiDate
INTO @VarForOutputIntoInsert
VALUES (101,N'ben', GETDATE());
--Display the result set of the table variable.
SELECT VarUserId, VarUserNm, VarModiDate FROM @VarForOutputIntoInsert;
- Here is a picture explanation of the OUTPUT clause.
MSSQL OUTPUT clause cautions
Transaction management.
- The OUTPUT clause can record the results that occur when changing data, but transactions must be properly managed when used.
Interaction with triggers.
- The OUTPUT clause can cause unexpected results when used within a trigger, so use it with caution.
Check if there is a performance issue.
- Using the OUTPUT clause when processing large amounts of data can cause performance degradation.
Leave a comment