MSSQL EXCEPT, INTERSECT Differences and Usage
EXCEPT and INTERSECT are set operators and have the same operation method as set difference and intersection that you learned in math class.
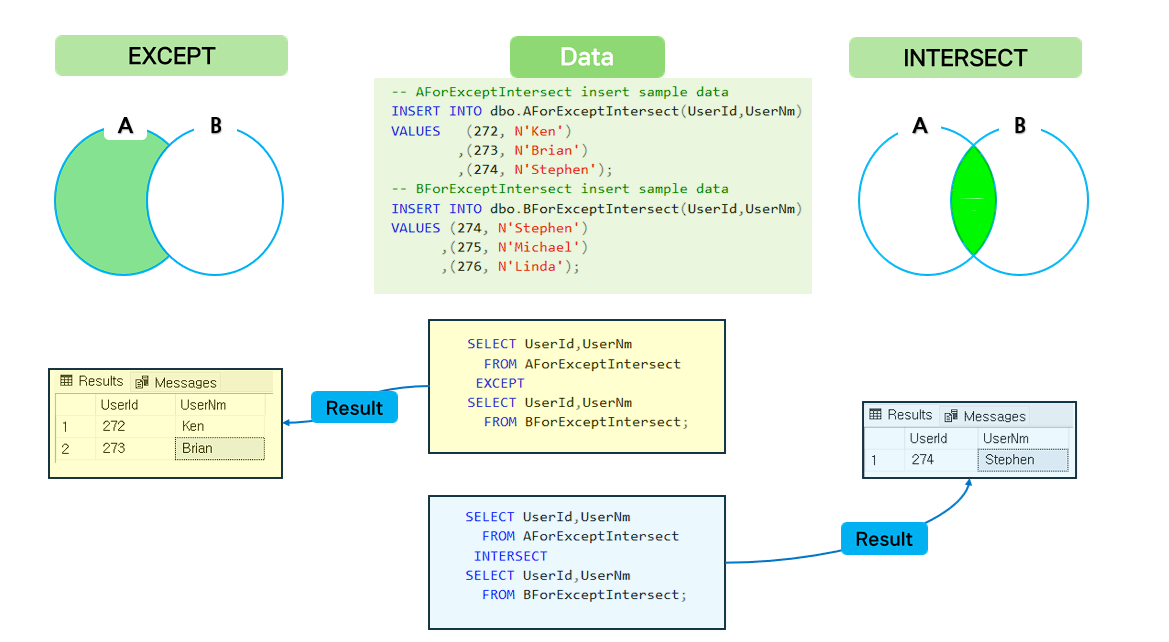
Features of EXCEPT, INTERSECT
- EXCEPT returns rows that are in the first query result but not in the second query.
- INTERSECT returns rows that are in both query results. In other words, it returns only common rows.
- The number and order of columns in the two queries must be the same for the operation to work.
- The data types returned from the queries must be compatible.
How to use EXCEPT, INTERSECT
EXCEPT source example.
- A common source for creating materials.
-- 1. EXCEPT,INTERSECT
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS AForExceptIntersect;
CREATE TABLE AForExceptIntersect (
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255)
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS BForExceptIntersect;
CREATE TABLE BForExceptIntersect (
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255)
);
-- AForExceptIntersect insert sample data
INSERT INTO dbo.AForExceptIntersect(UserId,UserNm)
VALUES (272, N'Ken')
,(273, N'Brian')
,(274, N'Stephen');
-- BForExceptIntersect insert sample data
INSERT INTO dbo.BForExceptIntersect(UserId,UserNm)
VALUES (274, N'Stephen')
,(275, N'Michael')
,(276, N'Linda');
- except source code.
SELECT UserId,UserNm
FROM AForExceptIntersect
EXCEPT
SELECT UserId,UserNm
FROM BForExceptIntersect;
INTERSECT source example.
- This is the intersect source code.
SELECT UserId,UserNm
FROM AForExceptIntersect
INTERSECT
SELECT UserId,UserNm
FROM BForExceptIntersect;
EXCEPT, INTERSECT execution result
- This is the result of EXCEPT, INTERSECT.
Leave a comment