Setting, Initializing, and Clearing MSSQL IDENTITY
In MSSQL, when an auto-increment column is required, IDENTITY is used, and IDENTITY columns are mostly used as the primary key of the created table.
Features of IDENTITY
- The value automatically increases whenever a new row is inserted.
- The IDENTITY column can set an initial value, which usually starts from 1.
- If you delete data in the middle, the IDENTITY value of the corresponding row will not be reused.
- You must use IDENTITY_INSERT to insert an empty IDENTITY value in the middle.
- You can check the IDENTITY auto-increment value using IDENT_INCR.
- You can check the last return value of IDENTITY using IDENT_CURRENT.
- Explains the difference between @@IDENTITY and SCOPE_IDENTITY().
How to use IDENTITY and examples
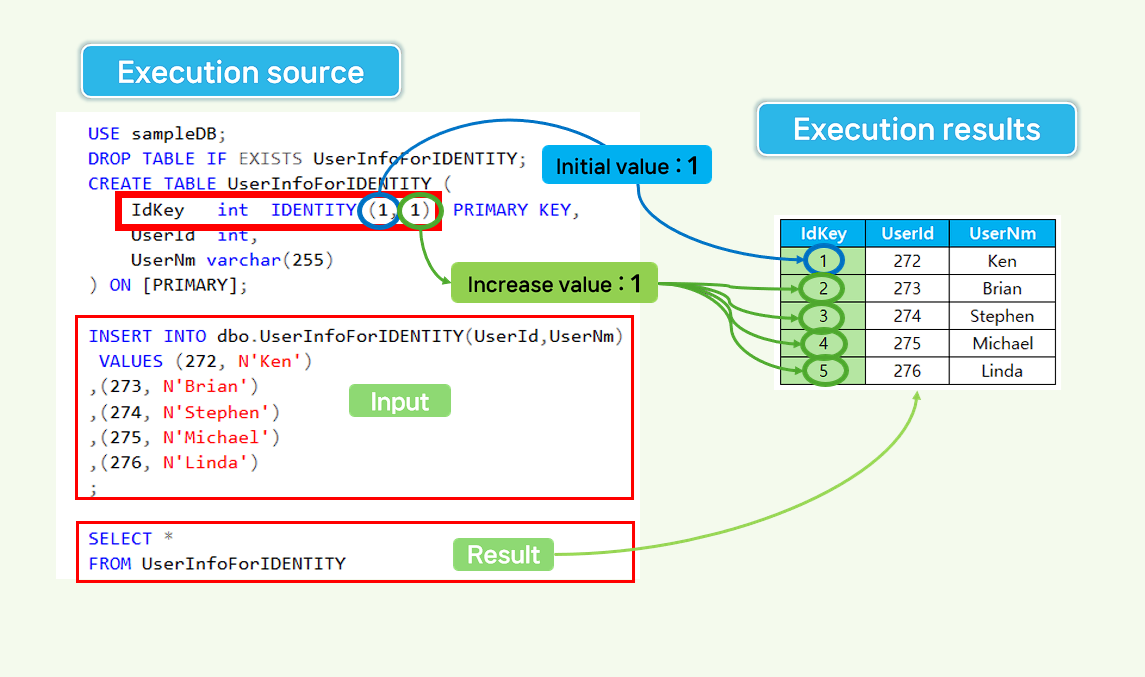
Auto-Increment setting.
- The IDENTITY column automatically increases in value. It starts at 1 and increases by 1 each time a row is inserted. - Set the id field to IDENTITY(1, 1) in the CREATE TABLE statement.
-- 1. auto-Increment setting increases by 1.
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS UserInfoForIDENTITY;
CREATE TABLE UserInfoForIDENTITY (
IdKey int IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255)
) ON [PRIMARY];
INSERT INTO dbo.UserInfoForIDENTITY(UserId,UserNm)
VALUES (272, N'Ken')
,(273, N'Brian')
,(274, N'Stephen')
,(275, N'Michael')
,(276, N'Linda')
;
SELECT *
FROM UserInfoForIDENTITY;
How to reuse IDENTITY using IDENTITY_INSERT.
- You can insert an IDENTITY value by using the SET IDENTITY_INSERT command to insert an IDENTITY value that is empty in the middle.
-- How to reuse IDENTITY using IDENTITY_INSERT.
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS UserInfoForIDENTITY;
CREATE TABLE UserInfoForIDENTITY (
IdKey int IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255)
) ON [PRIMARY];
INSERT INTO dbo.UserInfoForIDENTITY(UserId,UserNm)
VALUES (1, N'Ken')
,(273, N'Brian')
,(274, N'Stephen')
,(275, N'Michael')
,(276, N'Linda')
;
-- delete
DELETE
FROM UserInfoForIDENTITY
WHERE USERID IN ('273','274')
;
-- check
SELECT *
FROM UserInfoForIDENTITY;
-- IDENTITY_INSERT on
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].UserInfoForIDENTITY ON;
INSERT INTO [dbo].UserInfoForIDENTITY(IdKey,UserId,UserNm) VALUES (2,273, N'IDENTITY_INSERT1');
INSERT INTO [dbo].UserInfoForIDENTITY(IdKey,UserId,UserNm) VALUES (3,274, N'IDENTITY_INSERT2');
-- IDENTITY_INSERT off
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].UserInfoForIDENTITY OFF;
-- Check the result
SELECT *
FROM UserInfoForIDENTITY;
IDENT_SEED function.
- Used to check the initial value specified when creating an IDENTITY column in a table. - Changing the IDENTITY initial value using the DBCC CHECKIDENT command does not change the value returned by the IDENT_SEED function.
-- IDENT_SEED function.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS UserInfoForIDENT_SEED;
CREATE TABLE UserInfoForIDENT_SEED (
IdKey int IDENTITY (3, 5) PRIMARY KEY,
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255)
) ON [PRIMARY];
-- Check the result
SELECT IDENT_SEED('[dbo].UserInfoForIDENT_SEED') AS 'IDENT_SEED';
IDENT_INCR() function.
- Used to check for incremental values in tables that use IDENTITY.
--
CREATE TABLE UserInfoForIDENT_INCR (
IdKey int IDENTITY (1, 5) PRIMARY KEY,
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255)
) ON [PRIMARY];
-- Check the result
SELECT IDENT_INCR('[dbo].UserInfoForIDENT_INCR') AS 'IDENT_INCR';
IDENT_CURRENT() function.
- The IDENT_CURRENT function returns the most recently generated identity value for a specified table.
-- IDENT_CURRENT function.
CREATE TABLE UserInfoForIDENT_CURRENT (
IdKey int IDENTITY (1, 5) PRIMARY KEY,
UserId int,
UserNm varchar(255)
) ON [PRIMARY];
-- Check the result
SELECT IDENT_INCR('[dbo].UserInfoForIDENT_CURRENT') AS 'IDENT_CURRENT';
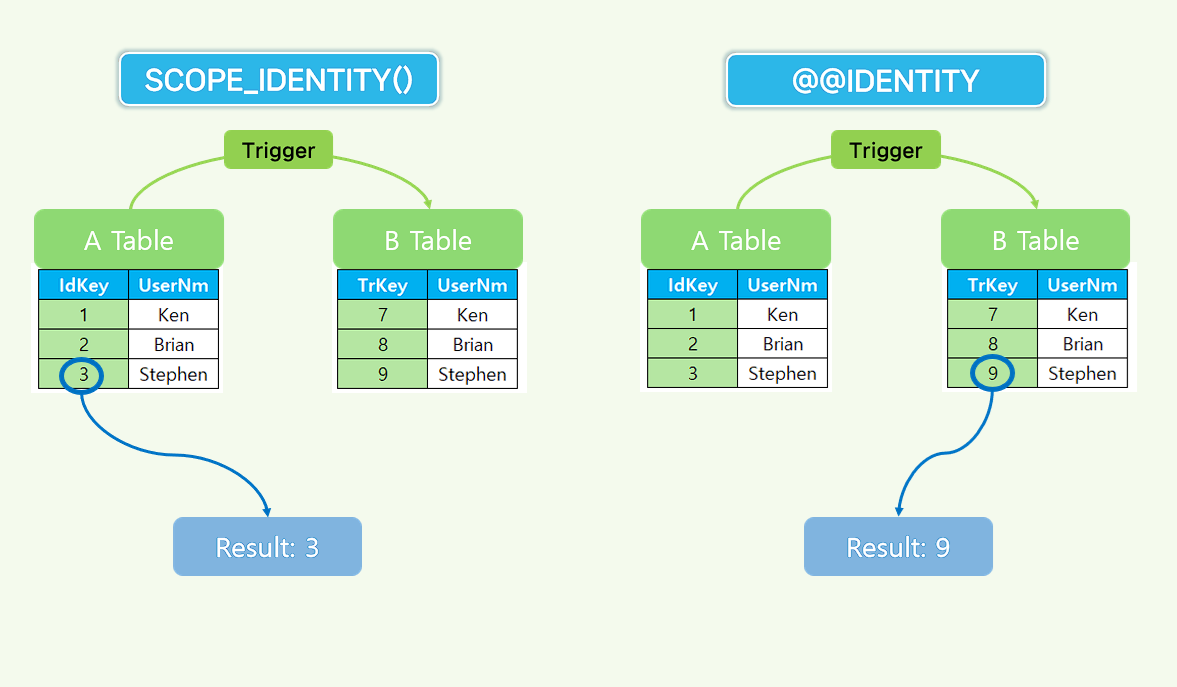
Difference between @@IDENTITY and SCOPE_IDENTITY().
- It is used similarly as a function that returns the IDENTITY value of the current session.
- It is thought of similarly as a function that returns the IDENTITY value of the current session, but when used as a trigger, the IDENTITY value is returned differently when checked.
- SCOPE_IDENTITY returns the IDENTITY value inserted within the current scope.
- @@IDENTITY returns the IDENTITY value without limiting it to a specific scope.
IDENTITY Cautions
- What about deleting data and IDENTITY values?
- If you delete intermediate data, the corresponding IDENTITY value will not be reused.
- In other words, the deleted IDENTITY value will not be refilled and will continue to increase.
- Therefore, there may be cases where the IDENTITY value is missing in the middle.
- The recovery method is to use the IDENTITY_INSERT function.
Leave a comment