How to use and explain the MSSQL FORMAT function
The FORMAT function allows users to specify formats for numeric and date data types more flexibly than other functions.
Features of the FORMAT function
- MSSQL is basically case-insensitive, but FORMAT function’s format is case-sensitive.
- Be careful when using it because it can cause performance issues when processing large amounts of data.
- FORMAT returns NULL for errors other than culture that are not valid.
- For example, if the value specified in format is invalid, NULL is returned.
Usage and Description of FORMAT Function
FORMAT Function Syntax
FORMAT( value, format [, culture ] ) ;
- value: An expression of a supported data type to format
- format: Must be a format supported by date string conversion, standard date and time format specifiers, standard number format strings, or custom number format strings.
- culture: If the culture argument is not specified, the language setting of the current session is used. The language can be changed using SET LANGUAGE.
Convert format using culture.
- You can convert the display format by entering the culture format.
DECLARE @DateFormat DATE = '11/22/2020';
SELECT FORMAT( @DateFormat, 'd', 'en-US' ) 'USA'
,FORMAT( @DateFormat, 'd', 'en-gb' ) 'British'
,FORMAT( @DateFormat, 'd', 'ko-kr' ) 'korea'
;
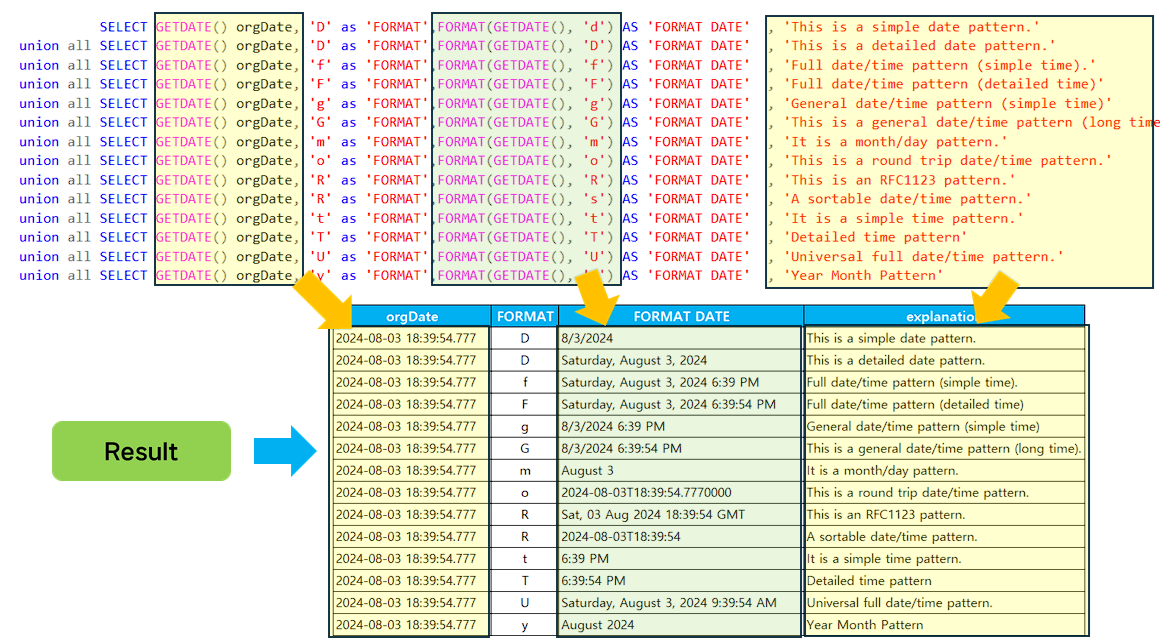
Convert standard date and time format strings.
- The example source adds output formats and descriptions for standard date and time format specifiers.
-- Standard date and time format strings
SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'D' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'd') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'This is a simple date pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'D' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'D') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'This is a detailed date pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'f' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'f') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'Full date/time pattern (simple time).' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'F' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'F') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'Full date/time pattern (detailed time)' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'g' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'g') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'General date/time pattern (simple time)' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'G' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'G') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'This is a general date/time pattern (long time).' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'm' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'm') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'It is a month/day pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'o' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'o') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'This is a round trip date/time pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'R' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'R') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'This is an RFC1123 pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'R' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 's') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'A sortable date/time pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 't' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 't') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'It is a simple time pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'T' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'T') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'Detailed time pattern' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'U' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'U') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'Universal full date/time pattern.' AS 'explanation'
union all SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, 'y' as 'FORMAT',FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'y') AS 'FORMAT DATE' , 'Year Month Pattern' AS 'explanation'
;
Custom date string conversion.
- You can use the FORMAT function when converting a date to a string.
- It has the advantage that the user can decide the order of year, month, day, and time.
SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'yyyy-MM-dd') AS formatType
union all
SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss') AS formatType
union all
SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss tt','en-US') AS formatType
union all
SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss tt','ko-kr') AS formatType
union all
SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'MM-dd-yyyy HH:mm:ss') AS formatType
union all
SELECT GETDATE() orgDate, FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'mm:ss dd-yyyy-MM HH') AS formatType
;
Convert standard number format strings.
- You can convert numeric formats using standard format specifiers supported by MSSQL.
SELECT * INTO FormatTable
FROM
(
SELECT 1.0002 AS VAL
UNION ALL SELECT 1.55 AS VAL
UNION ALL SELECT 1.99 AS VAL
UNION ALL SELECT -1.4263 AS VAL
UNION ALL SELECT 25.2784 AS VAL
UNION ALL SELECT 10 AS VAL
) P1;
-- Convert standard number format strings
SELECT VAL ORG_VAL
,FORMAT(VAL, 'C', 'en-us') AS 'USA Currency'
,FORMAT(VAL, 'C', 'ko-kr') AS 'korea Currency'
,FORMAT(1023, 'd','ko-kr') AS 'Supports only integers'
,FORMAT(VAL, 'D','ko-kr') AS 'Supports only integers'
,FORMAT(VAL, 'F5', 'en-us') AS 'Display 5 decimal places'
,FORMAT(VAL, 'G10', 'en-us') AS 'Display significant digits'
,FORMAT(VAL, 'N', 'en-us') AS 'All number formats'
FROM FormatTable
;
Convert a custom numeric format string.
- Custom numeric format string conversion mainly uses shop(#) and number zero(0).
SELECT FORMAT(123456789012, '###,###') AS 'Thousands display'
,FORMAT(1234567890.927, '0.00') AS 'Decimal display'
;
FORMAT function performance
- The FORMAT function is more flexible than the cast and convert functions, so it is easier to use, but it has performance issues when processing large amounts of data because it performs string operations internally.
Leave a comment