How to use MSSQL ORDER BY
ORDER BY is used to sort and output data retrieved with a SELECT statement based on a specific column for various purposes.
ORDER BY Features
- You can sort the query result set by a specified list of columns and optionally limit the returned rows to a specified range.
- If you do not specify an ORDER BY clause, the order in which rows are returned in the result set is not guaranteed.
- The ranking function determines the order in which the DATA set is applied.
- Column sorting can be specified by name, column alias, or by a non-negative integer representing the position of the column in the SELECT list.
- Column names must be unique to use order by.
- The result set is sorted by the first column, then this sorted list is sorted by the second column, and so on.
- COLLATE can only be applied to columns of type char, varchar, nchar, and nvarchar.
- Specifies whether the values ??in the specified column are sorted in ascending or descending order.
- ASC sorts in ascending order, and DESC sorts in descending order. ASC is the default sort order.
- Null values ??are treated as the smallest possible value.
How to use ORDER BY
Basic ORDER BY usage.
- Syntax.
[ ORDER BY
{
order_by_expression
[ ASC | DESC ]
} [ ,...n ]
]
- Source code
-- Basic ORDER BY usage
USE sampleDB;
GO
SELECT scoreyyyymm,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE studentNm LIKE '%A%'
AND scoreyyyymm = '202401'
ORDER BY studentNm;
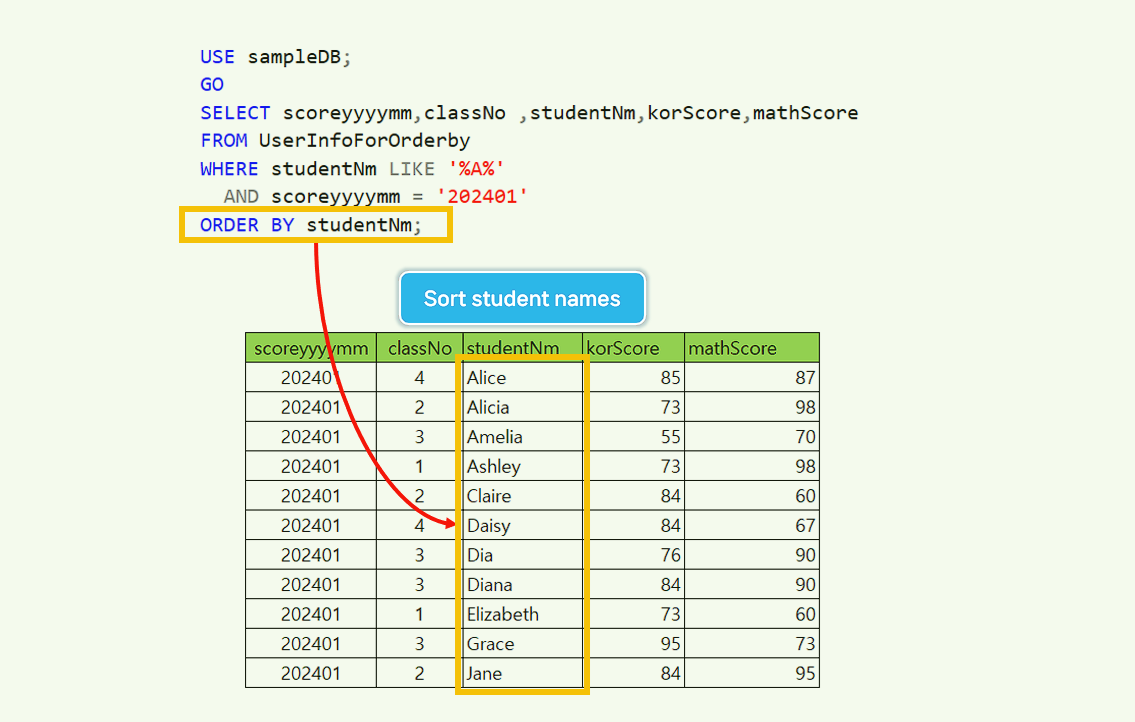
ORDER BY Sorting method by column number and alias.
- After specifying a column alias, specify it as the sort order column in order by column.
-- How to sort by column number and alias
USE sampleDB;
GO
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo num ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE studentNm LIKE '%A%'
ORDER BY num,4 desc;
ORDER BY Specifies both ascending and descending order.
- Sorted in ascending order by the korScore column and then in descending order by the mathScore column.
-- Specify both ascending and descending order
USE sampleDB;
GO
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE studentNm LIKE '%A%'
ORDER BY korScore asc,mathScore desc;
ORDER BY Conditional ordering.
- Use a CASE expression in the ORDER BY clause to conditionally determine the sort order of rows based on specified column values.
-- Conditional ordering
USE sampleDB;
GO
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE studentNm LIKE '%A%'
ORDER BY CASE classNo WHEN 1 THEN korScore END DESC
,CASE WHEN classNo = 2 THEN mathScore END;
Using ORDER BY in ranking function.
- You can use the ORDER BY clause with the ranking functions ROW_NUMBER, RANK, DENSE_RANK, and NTILE.
SELECT classNo,studentNm,korScore
,RANK() OVER (ORDER BY classNo asc, korScore DESC ) AS winFuncRank
,DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY classNo asc, korScore DESC ) AS winFuncDenseRank
,ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY classNo asc, korScore DESC ) AS winFuncRowNum
,NTILE(4) OVER (ORDER BY classNo asc, korScore DESC ) AS Quartile
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE scoreyyyymm = '202401';
Limit the number of rows returned.
- Specify OFFSET and FETCH values ??using integer constants.
-- Specifying OFFSET and FETCH values ??using integer constants
USE sampleDB;
GO
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE scoreyyyymm = '202401'
ORDER BY classNo ,studentNm OFFSET 6 ROWS;
USE sampleDB;
GO
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE scoreyyyymm = '202401'
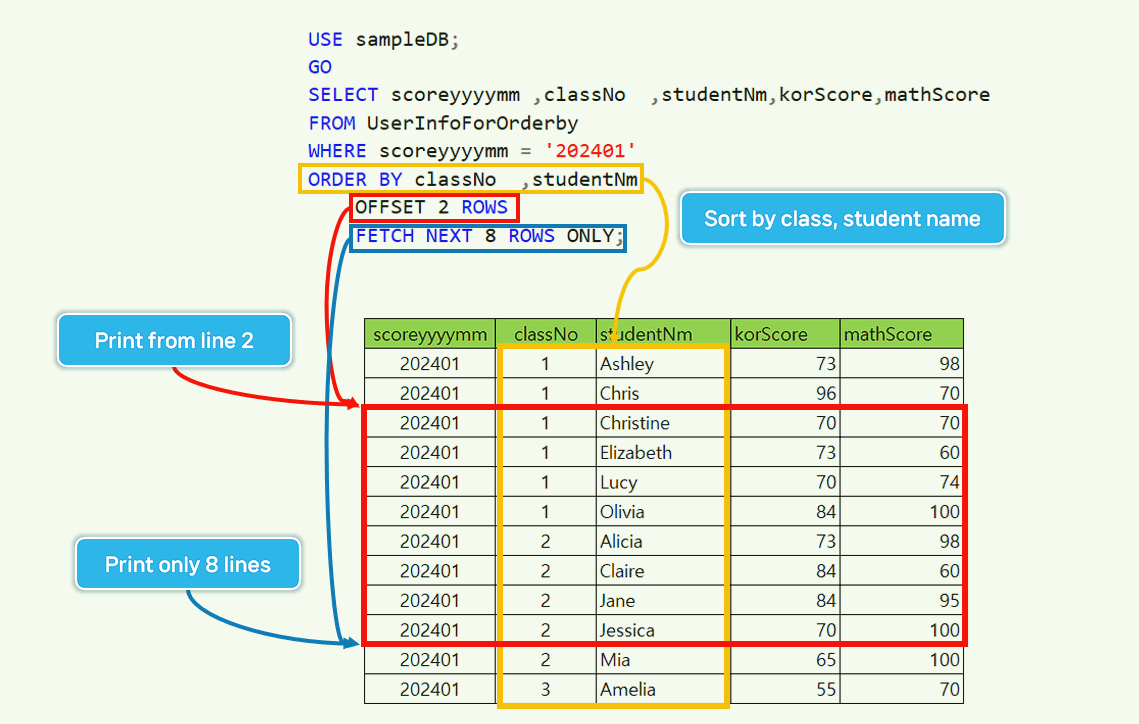
ORDER BY classNo ,studentNm
OFFSET 2 ROWS
FETCH NEXT 8 ROWS ONLY;
- Specifying OFFSET and FETCH values ??using variables.
-- Specifying OFFSET and FETCH values ??using variables
USE sampleDB;
GO
-- Specifying variables for OFFSET and FETCH values
DECLARE @RowsToSkip TINYINT = 2
, @FetchRows TINYINT = 8;
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE scoreyyyymm = '202401'
ORDER BY classNo ,studentNm
OFFSET @RowsToSkip ROWS
FETCH NEXT @FetchRows ROWS ONLY;
How to use ORDER BY with UNION, EXCEPT and INTERSECT.
- UNION example.
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE scoreyyyymm = '202401'
-- ORDER BY cannot be specified here.
union all
SELECT scoreyyyymm ,classNo ,studentNm,korScore,mathScore
FROM UserInfoForOrderby
WHERE scoreyyyymm = '202401'
ORDER BY classNo ,studentNm
Restrictions on the ORDER BY clause
- There is no limit to the number of columns in the ORDER BY clause, but the total size of the columns specified in the ORDER BY clause cannot exceed 8,060 bytes.
- Columns of type ntext, text, image, geography, geometry, and xml cannot be used in the ORDER BY clause.
- Integers or constants cannot be specified when appearing in the ranking function (in the OVER clause).
- In queries that use the UNION, EXCEPT, or INTERSECT operators, ORDER BY can only be used at the end of the statement.
- The ORDER BY clause cannot be used in views, inline functions, derived tables, and subqueries unless the TOP clause or the OFFSET and FETCH clauses are also specified.
- The OVER clause does not support OFFSET and FETCH.
- OFFSET and FETCH cannot be specified directly in INSERT, UPDATE, MERGE, and DELETE statements, but can be specified in the sub Query defined in these statements.
- For INSERT INTO SELECT statements, OFFSET and FETCH can be specified in the SELECT statement.
- In queries that use the UNION, EXCEPT, or INTERSECT operators, OFFSET and FETCH can be specified only in the last query, which specifies the order of the query results.
Leave a comment