How to use database DELETE DML
We will explain the DELETE DML statement used to delete data in a TABLE.
DELETE DML basic structure
Using the FROM clause.
- syntax code
DELETE
FROM [TABLE name]
WHERE [conditional statement];
How to delete after omitting the FROM clause.
- syntax code
DELETE [TABLE name]
WHERE [conditional statement];
Example of DELETE DML statement usage
How to clear TABLE with basic structure.
Question:Please DELETE all contents of the UserInfoForDelete table.
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS UserInfoForDelete;
CREATE TABLE UserInfoForDelete (
UserId int NOT NULL,
UserNm varchar(255),
UserAge int
);
insert into UserInfoForDelete(UserId,UserNm,UserAge)
values
('202401','kim',60),
('202402','lee',84),
('202403','park',90),
('202404','moon',65),
('202405','young',35),
('202406','cho',45)
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS BoardJoinDelete;
CREATE TABLE BoardJoinDelete (
BoardNo int NOT NULL,
BoardTitle varchar(255),
UserId int
);
insert into BoardJoinDelete(BoardNo,BoardTitle,UserId)
values
(1,'seoul',202401),
(2,'busun',202402),
(3,'inchen',202404)
-- 1. How to clear TABLE with basic structure.
-- Check if data exists
SELECT * FROM UserInfoForDelete;
-- Delete Data
delete FROM UserInfoForDelete;
-- Check if the deletion was successful
SELECT * FROM UserInfoForDelete;
How to delete data by joining with another table.
Question:Join the registered ID of UserInfoForDelete and DELETE the data of BoardJoinDelete.
-- 2. How to DELETE by joining with another table.
-- Example 1
DELETE BD
FROM BoardJoinDelete BD
JOIN UserInfoForDelete UD
ON BD.UserId = UD.UserId;
-- Example 2
DELETE BoardJoinDelete
FROM BoardJoinDelete BD
JOIN UserInfoForDelete UD
ON BD.UserId = UD.UserId;

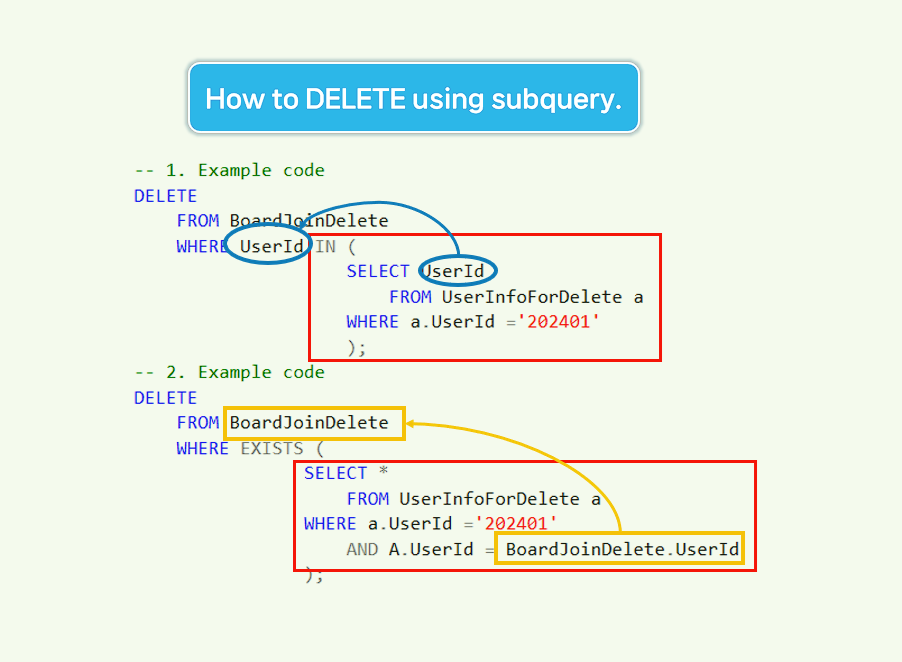
How to delete data using subquery.
Question:Use Sub Query to DELETE the bulletin board data of the member whose UserId is ‘202401’ in UserInfoForDelete.
-- 3. How to delete data using subquery.
-- Example 1
DELETE
FROM BoardJoinDelete
WHERE UserId IN (
SELECT UserId
FROM UserInfoForDelete a
WHERE a.UserId ='202401'
);
-- Example 2
DELETE
FROM BoardJoinDelete
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT *
FROM UserInfoForDelete a
WHERE a.UserId ='202401'
AND A.UserId = BoardJoinDelete.UserId
);
How to limit the number of rows deleted using TOP.
The TOP(n) clause in a DELETE statement allows you to randomly select n rows for deletion.
Question:Delete only two items of UserInfoForDelete using Top.
-- 4. How to limit the number of rows deleted using TOP.
DELETE TOP(2)
FROM UserInfoForDelete
WHERE UserId LIKE '2024%'
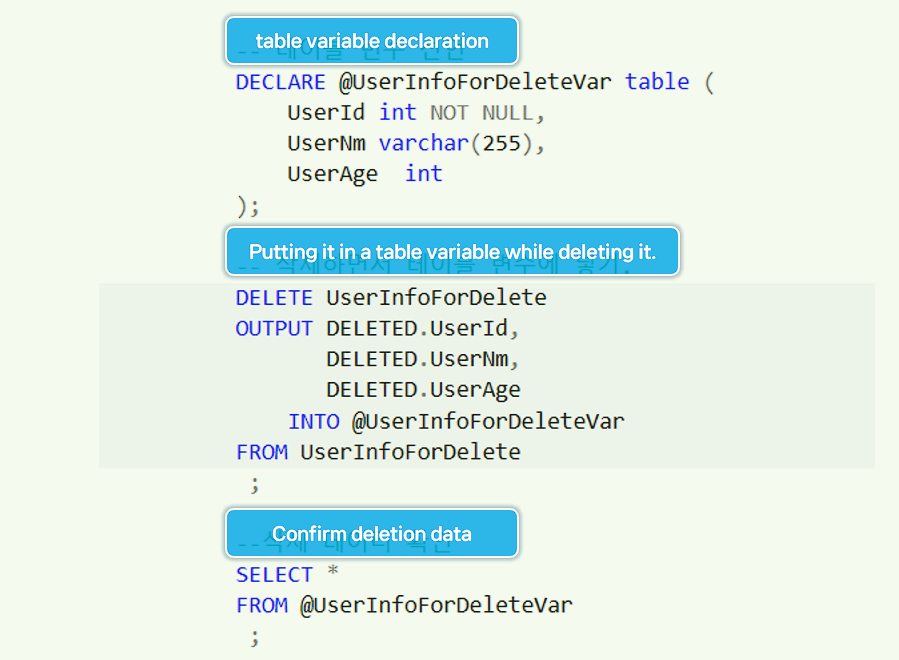
Check deleted data using OUTPUT in the DELETE statement.
Question:Enter the deleted data into the table variable and check the deleted data.
-- 5. Check deleted data using OUTPUT in the DELETE statement.
-- table variable declaration
DECLARE @UserInfoForDeleteVar table (
UserId int NOT NULL,
UserNm varchar(255),
UserAge int
);
-- Putting it in a table variable while deleting it.
DELETE UserInfoForDelete
OUTPUT DELETED.UserId,
DELETED.UserNm,
DELETED.UserAge
INTO @UserInfoForDeleteVar
FROM UserInfoForDelete
;
--Confirm deletion data
SELECT *
FROM @UserInfoForDeleteVar
;
DELETE DML statement precautions
Unconditional DELETE DML statement.
Executing an unconditional DELETE DML statement deletes all records in that table.
It is a good idea to check deleted DATA using table variables and OUTPUT.
Use transactions in DELETE DML.
Since the DELETE DML statement means permanent deletion of data, DBAs use rollbacks using transactions to prevent mistakes.
Use WHERE in DELETE DML.
When executing a DELETE DML statement, it is important to clearly specify the WHERE condition to limit the target DATA to be deleted.
Leave a comment