Create, Delete, and explain MSSQL default constraints
If you set the default constraint on the Column, it is a constraint that puts the value into the field when entering the record as the default value set to default.
Default constraint concept
- This is how to set the default value using constraints on the column.
- This automatically fills the default value without specifying a value for that column when you add data in the future.
- For example, in girls high school, the default of the column that puts gender in the academic related table can be set to female.
How to generate a DEFAULT constraint
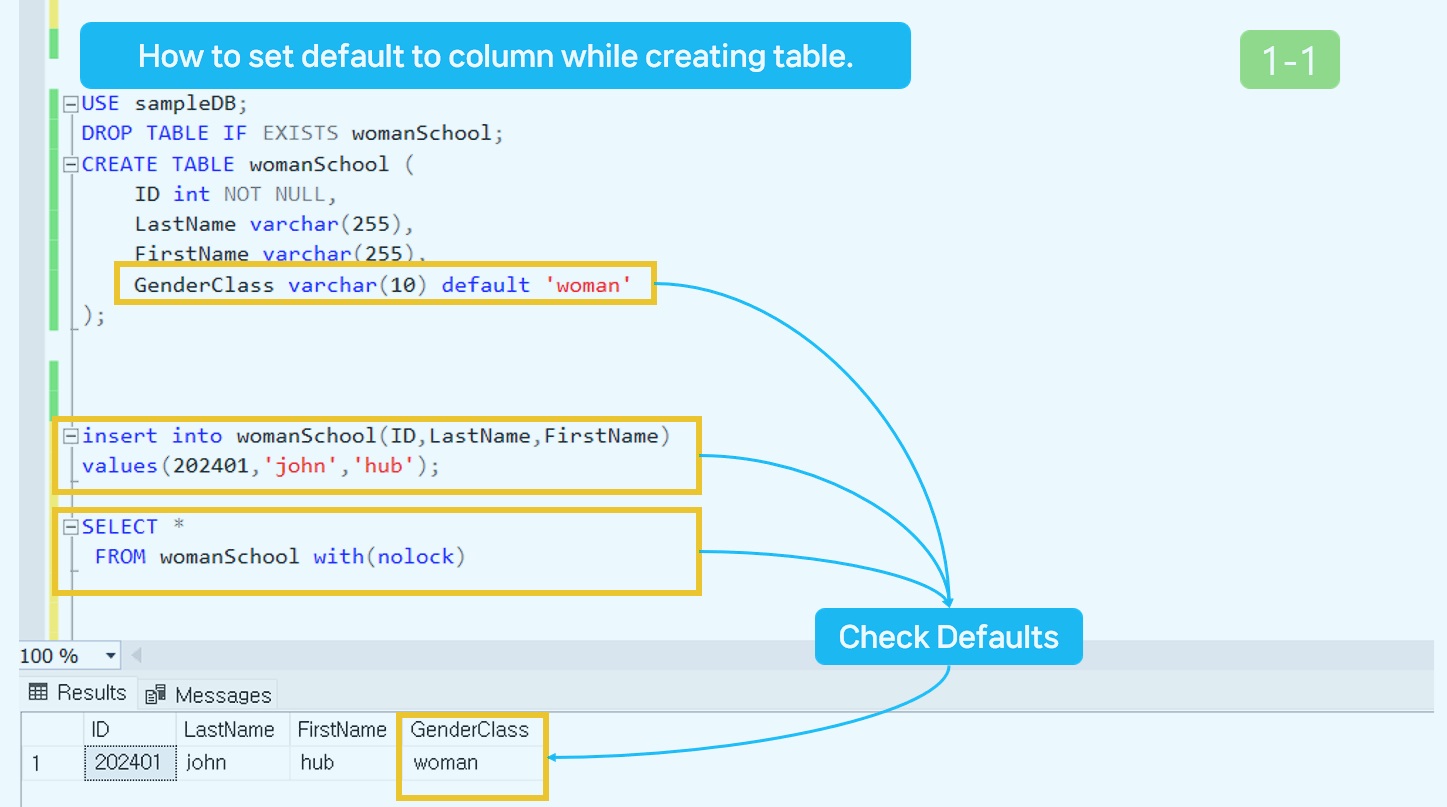
1. How to set default to column while creating a table.
Syntax and Source code.
CREATE TABLE [Table Name] (
[column1] [dataType],
[column1] [dataType] DEFAULT 'Default value',
[column3] [dataType],
);
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS womanSchool;
CREATE TABLE womanSchool (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255),
FirstName varchar(255),
GenderClass varchar(10) default 'woman'
);
-- Insert
insert into womanSchool(ID,LastName,FirstName)
values(202401,'john','hub');
SELECT *
FROM womanSchool with(nolock);
Results of executing source code.
2. How to create a dafault after creating a table.
Syntax and Source code.
-- Syntax
ALTER TABLE [Table Name]
ADD CONSTRAINT [Constraint name] DEFAULT ('Default value') FOR [column name];
-- Source code.
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS womanSchool;
CREATE TABLE womanSchool (
ID int NOT NULL,
GenderClass varchar(10)
);
ALTER TABLE [womanSchool]
ADD CONSTRAINT [df_womanSchool_GenderClass] DEFAULT ('woman') FOR [GenderClass];
3. How to set default when adding a new column.
There are cases where the dafault name is automatically generated and cannot be managed later. It is recommended to set the dafault after creating the column.
Syntax and Source code.
-- Syntax
ALTER TABLE [Table Name] ADD [column1] [dataType] DEFAULT [Default value];
-- Source code.
USE sampleDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS womanSchool;
CREATE TABLE womanSchool (
ID int NOT NULL
);
ALTER TABLE [womanSchool] ADD GenderClass varchar(10) DEFAULT 'woman';
insert into womanSchool(ID)
values(202401);
SELECT *
FROM womanSchool with(nolock);
How to check DEFAULT constraints
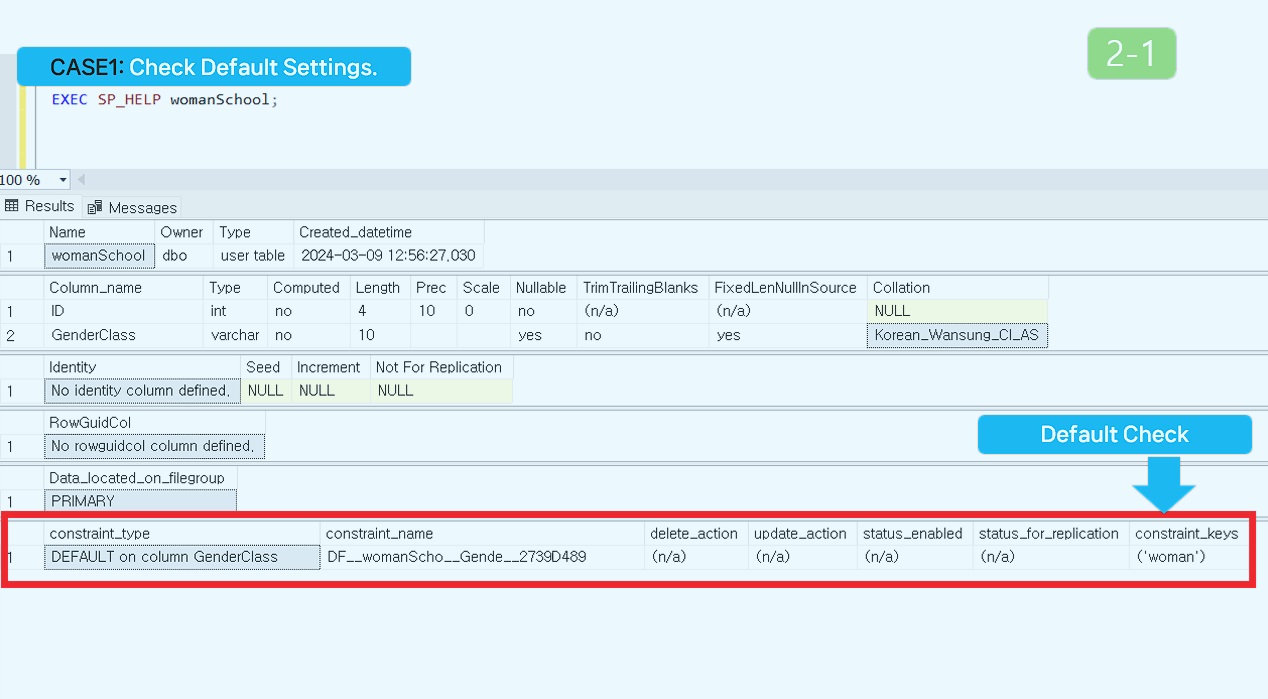
Using SP_HELP to Check Constraints
Syntax and Source code.
-- Syntax
EXEC SP_HELP[Table Name]
-- CASE1: Source code.
EXEC SP_HELP womanSchool;
Results of executing source code.
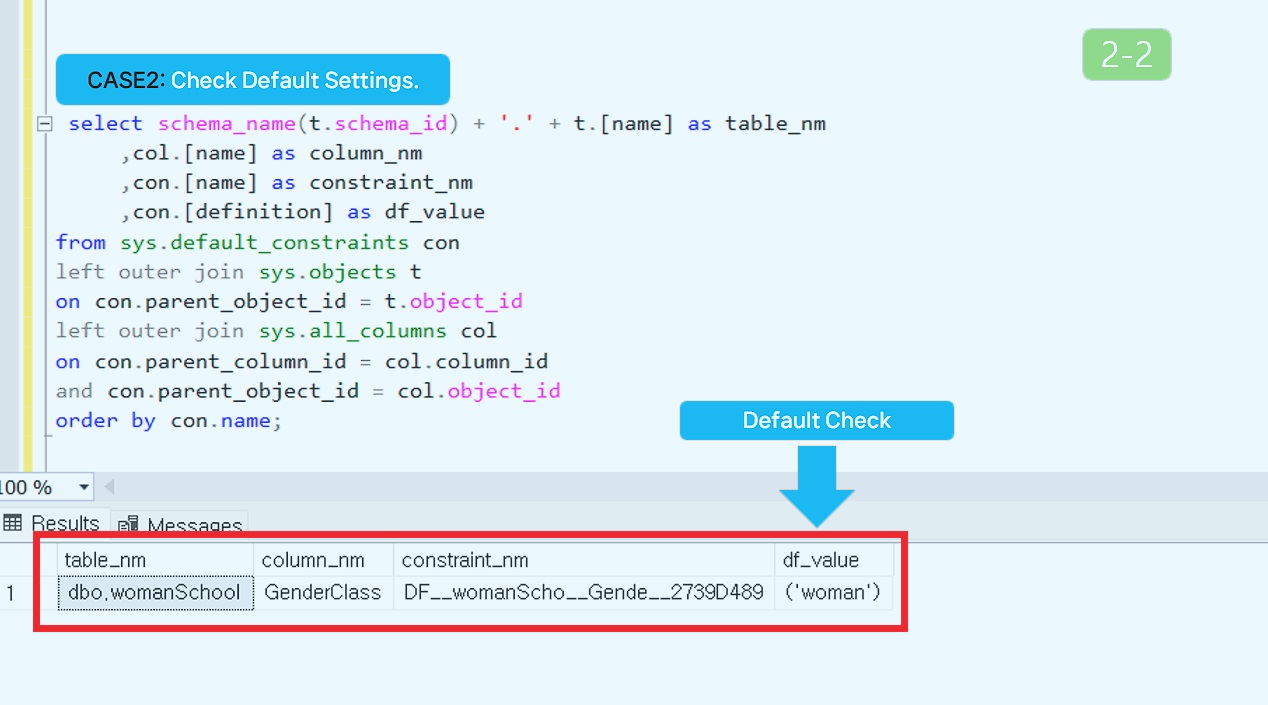
Using Schema to Check Constraints
Syntax and Source code.
-- CASE2: Source code.
select schema_name(t.schema_id) + '.' + t.[name] as table_nm
,col.[name] as column_nm
,con.[name] as constraint_nm
,con.[definition] as df_value
from sys.default_constraints con
left outer join sys.objects t
on con.parent_object_id = t.object_id
left outer join sys.all_columns col
on con.parent_column_id = col.column_id
and con.parent_object_id = col.object_id
order by con.name;
Results of executing source code.
Drop the default constraints
Syntax and Source code.
-- Syntax
ALTER TABLE [Table Name] DROP CONSTRAINT [Constraint name];
-- Source code.
ALTER TABLE womanSchool DROP df_womanSchool_GenderClass;
Leave a comment